The effects of two-stage carotid occlusion on spatial memory and pro-inflammatory markers in the hippocampus of rats
- PMID: 27470129
- PMCID: PMC10717598
- DOI: 10.1007/s12576-016-0474-z
The effects of two-stage carotid occlusion on spatial memory and pro-inflammatory markers in the hippocampus of rats
Abstract
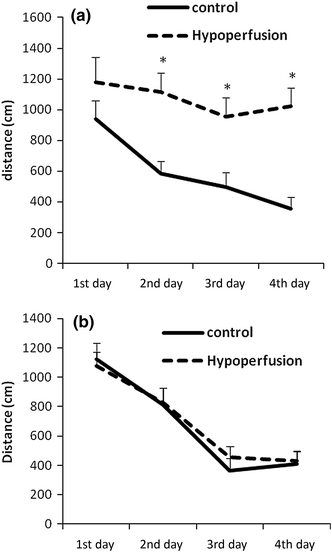
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of cerebral hypoperfusion on cognitive ability, TNFα, IL1β and PGE2 levels in both hippocampi in a modified two-vessel occlusion model. Both common carotid arteries of adult male Wistar rats were permanently occluded with an interval of 1 week between occlusions. Learning and memory were significantly decreased after 1 month. This reduction was not significant after 2 months, which may be attributed to blood flow compensation. The TNFα level was significantly increased after 3 h and 1 day. IL1β was significantly increased after 1 day. After a week there was no significant difference in pro-inflammatory levels. Furthermore, there was no difference between right and left hippocampi. It is possible that TNFα and IL1β elevation initiates pathologic processes that contribute to memory impairment.
Keywords: Cerebral hypoperfusion; Hippocampus; Inflammation; Interleukins; Spatial memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Wang J, Zhang HY, Tang XC. Huperzine a improves chronic inflammation and cognitive decline in rats with cerebral hypoperfusion. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(4):807–815. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

