Endocytosis regulates membrane localization and function of the fusogen EFF-1
- PMID: 27470417
- PMCID: PMC5584736
- DOI: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1211399
Endocytosis regulates membrane localization and function of the fusogen EFF-1
Abstract
Cell fusion is essential for sexual reproduction and formation of muscles, bones, and placenta. Two families of cell fusion proteins (Syncytins and FFs) have been identified in eukaryotes. Syncytins have been shown to form the giant syncytial trophoblasts in the placenta. The FFs are essential to fuse cells in the skin, reproductive, excretory, digestive and nervous systems in nematodes. EFF-1 (Epithelial Fusion Failure 1), a member of the FF family, is a type I membrane glycoprotein that is essential for most cell fusions in C. elegans. The crystal structure of EFF-1 ectodomain reveals striking structural similarity to class II fusion glycoproteins from enveloped viruses (e.g. dengue and rubella) that mediate virus to cell fusion. We found EFF-1 to be present on the plasma membrane and in RAB-5-positive early endosomes, with EFF-1 recycling between these 2 cell compartments. Only when EFF-1 proteins transiently arrive to the surfaces of 2 adjacent cells do they dynamically interact in trans and mediate membrane fusion. EFF-1 is continuously internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis via the activity of 2 small GTPases: RAB-5 and Dynamin. Here we propose a model that explains how EFF-1 endocytosis together with interactions in trans can control cell-cell fusion. Kontani et al. showed that vacuolar ATPase (vATPase) mutations result in EFF-1-dependent hyperfusion. 1 We propose that vATPase is required for normal degradation of EFF-1. Failure to degrade EFF-1 results in delayed hyperfusion and mislocalization to organelles that appear to be recycling endosomes. EFF-1 is also required to fuse neurons as part of the repair mechanism following injury and to prune dendrites. We speculate that EFF-1 may regulate neuronal tree like structures via endocytosis. Thus, endocytosis of cell-cell fusion proteins functions to prevent merging of cells and to sculpt organs and neurons.
Keywords: AFF-1; C. elegans; Dynamin; EFF-1; RAB-5; cell-cell fusion; endocytosis; vacuolar ATPase.
Figures
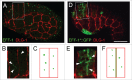

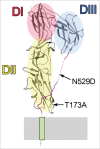
Similar articles
-
RAB-5- and DYNAMIN-1-Mediated Endocytosis of EFF-1 Fusogen Controls Cell-Cell Fusion.Cell Rep. 2016 Feb 16;14(6):1517-1527. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.01.027. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26854231 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of RAB-5 Increases EFF-1 Fusogen Availability at the Cell Surface and Promotes the Regenerative Axonal Fusion Capacity of the Neuron.J Neurosci. 2019 Apr 10;39(15):2823-2836. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1952-18.2019. Epub 2019 Feb 8. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30737314 Free PMC article.
-
The EFF-1A Cytoplasmic Domain Influences Hypodermal Cell Fusions in C. elegans But Is Not Dependent on 14-3-3 Proteins.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 22;11(1):e0146874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146874. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26800457 Free PMC article.
-
Cell fusion.WormBook. 2006 Jan 6:1-32. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.52.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell fusion: EFF is enough.Curr Biol. 2005 Apr 12;15(7):R252-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.03.020. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15823525 Review.
Cited by
-
Extrinsic Repair of Injured Dendrites as a Paradigm for Regeneration by Fusion in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2017 May;206(1):215-230. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.196386. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28283540 Free PMC article.
-
EFF-1 fusogen promotes phagosome sealing during cell process clearance in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;20(4):393-399. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0068-5. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Nat Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29556089 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Fusion: Merging Membranes and Making Muscle.Trends Cell Biol. 2019 Dec;29(12):964-973. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2019.09.002. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Trends Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31648852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fusogen-mediated neuron-neuron fusion disrupts neural circuit connectivity and alters animal behavior.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 15;117(37):23054-23065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1919063117. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32855296 Free PMC article.
-
An SNX10-dependent mechanism downregulates fusion between mature osteoclasts.J Cell Sci. 2021 May 1;134(9):jcs254979. doi: 10.1242/jcs.254979. Epub 2021 May 11. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 33975343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kontani K, Moskowitz IPG, Rothman JH. Repression of cell-cell fusion by components of the C. elegans vacuolar ATPase complex. Dev Cell 2005; 8:787-94; PMID:15866168; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.02.018 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mohler WA, Shemer G, del Campo JJ, Valansi C, Opoku-Serebuoh E, Scranton V, Assaf N, White JG, Podbilewicz B. The type I membrane protein EFF-1 is essential for developmental cell fusion. Dev Cell 2002; 2:355-62; PMID:11879640; https://doi.org/10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00129-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gattegno T, Mittal A, Valansi C, Nguyen KCQ, Hall DH, Chernomordik LV, Podbilewicz B. Genetic control of fusion pore expansion in the epidermis of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell 2007; 18:1153-1166; PMID:17229888; https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E06-09-0855 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Podbilewicz B, Leikina E, Sapir A, Valansi C, Suissa M, Shemer G, Chernomordik LV. The C. elegans Developmental Fusogen EFF-1 Mediates Homotypic Fusion in Heterologous Cells and In Vivo. Dev Cell 2006; 11:471-81; PMID:17011487; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2006.09.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shinn-Thomas JH, Del Campo JJ, Wang J, Mohler WA. The EFF-1A Cytoplasmic Domain Influences Hypodermal Cell Fusions in C. elegans But Is Not Dependent on 14-3-3 Proteins. PLoS One 2016; 11(1):e0146874; PMID:26800457; https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146874 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
