Essential Role of Smooth Muscle STIM1 in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Dysfunction
- PMID: 27470514
- PMCID: PMC5061131
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307869
Essential Role of Smooth Muscle STIM1 in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Dysfunction
Abstract
Objectives: Chronic hypertension is the most critical risk factor for cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and stroke.
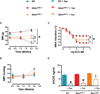
Approach and results: Here we show that wild-type mice infused with angiotensin II develop hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy, perivascular fibrosis, and endothelial dysfunction with enhanced stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) expression in heart and vessels. All these pathologies were significantly blunted in mice lacking STIM1 specifically in smooth muscle (Stim1(SMC-/-)). Mechanistically, STIM1 upregulation during angiotensin II-induced hypertension was associated with enhanced endoplasmic reticulum stress, and smooth muscle STIM1 was required for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced vascular dysfunction through transforming growth factor-β and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-dependent pathways. Accordingly, knockout mice for the endoplasmic reticulum stress proapoptotic transcriptional factor, CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP(-/-)), were resistant to hypertension-induced cardiovascular pathologies. Wild-type mice infused with angiotensin II, but not Stim1(SMC-/-) or CHOP(-/-) mice showed elevated vascular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activity and reduced phosphorylated endothelial nitric oxide synthase, cGMP, and nitrite levels.
Conclusions: Thus, smooth muscle STIM1 plays a crucial role in the development of hypertension and associated cardiovascular pathologies and represents a promising target for cardiovascular therapy.
Keywords: ER stress; cardiac hypertrophy; endothelial nitric oxide synthase; hypertension; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; stromal interaction molecule 1; vascular reactivity.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures



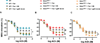
References
-
- Efrati S, Zaidenstein R, Dishy V, Beberashvili I, Sharist M, Averbukh Z, Golik A, Weissgarten J. Ace inhibitors and survival of hemodialysis patients. American journal of kidney diseases. 2002;40:1023–1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

