Role of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling in depression and dietary intake of glucoraphanin confers stress resilience in mice
- PMID: 27470577
- PMCID: PMC4965765
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30659
Role of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling in depression and dietary intake of glucoraphanin confers stress resilience in mice
Abstract
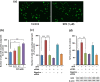
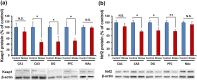
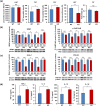
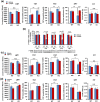
The transcription factor Keap1-Nrf2 system plays a key role in inflammation which is involved in depression. We found lower expression of Keap1 and Nrf2 proteins in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), CA3 and dentate gyrus (DG) of hippocampus in mice with depression-like phenotype compared to control mice. Serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in Nrf2 knock-out (KO) mice were higher than those of wild-type mice, suggestive of enhanced inflammation in KO mice. Decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its receptor tropomyosin-receptor-kinase B (TrkB) signaling in the PFC, CA3 and DG plays a role in the depression-like phenotype of Nrf2 KO mice. TrkB agonist 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, but not antagonist ANA-12, produced antidepressant effects in Nrf2 KO mice, by stimulating TrkB in the PFC, CA3 and DG. Pretreatment with Nrf2 activator sulforaphane (SFN) prevented the depression-like phenotype induced after repeated social defeat stress. Interestingly, dietary intake of 0.1% glucoraphanin (a precursor of SFN) containing food during juvenile and adolescent stages also prevented the depression-like phenotype evoked in adulthood, after repeated social defeat stress. These findings suggest that Keap1-Nrf2 system plays a key role in depression and that dietary intake of SFN-rich food during juvenile stages and adolescence can confer stress resilience in adulthood.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs H. Suganuma and Y. Ushida are employee of KAGOME CO., LTD which provides GF-rich extract powder. The other authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Essential Role of Keap1-Nrf2 Signaling in Mood Disorders: Overview and Future Perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 16;9:1182. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01182. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30386243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Intake of Sulforaphane-Rich Broccoli Sprout Extracts during Juvenile and Adolescence Can Prevent Phencyclidine-Induced Cognitive Deficits at Adulthood.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 24;10(6):e0127244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127244. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26107664 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant effects of TrkB ligands on depression-like behavior and dendritic changes in mice after inflammation.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Oct 31;18(4):pyu077. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu077. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25628381 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin gallate upregulates NRF2 to prevent diabetic nephropathy via disabling KEAP1.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jul;108:840-857. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.04.365. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28457936
-
Glucoraphanin: a broccoli sprout extract that ameliorates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance.Adipocyte. 2018;7(3):218-225. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2018.1474669. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Adipocyte. 2018. PMID: 29898626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Dietary Supplement, Carvacrol, Alleviates LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress, Neurodegeneration, and Depressive-Like Behaviors via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Apr 8;14:1313-1329. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S294413. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. Retraction in: J Inflamm Res. 2022 Nov 07;15:6071-6072. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S395890. PMID: 33854358 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Dietary glucoraphanin prevents the onset of psychosis in the adult offspring after maternal immune activation.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 1;8(1):2158. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20538-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29391571 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience Dysregulation in Major Depressive Disorder: Focus on Glutamatergic Imbalance and Microglial Activation.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018 Mar 5;16(3):297-307. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170630164715. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28676011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant actions of arketamine: beyond the NMDA receptor.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Jan;27(1):559-573. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01121-1. Epub 2021 May 7. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 33963284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2 regulates the arginase 1+ microglia phenotype through the initiation of TREM2 transcription, ameliorating depression-like behavior in mice.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 31;12(1):459. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02227-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36316319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whiteford H. A. et al.. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 382, 1575–1586 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Mukakami K. & Sasaki S. Dietary intake and depressive symptoms: a systemic review of observational studies. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54, 471–488 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Bazinet R. P. & Layé S. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their metabolites in brain function and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 15, 771–785 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Mello A. H. et al.. ω-3 and major depression: a review. Acta Neuropsychiatr 26, 178–185 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

