Collaborative Interferon-γ and Interleukin-17 Signaling Protects the Oral Mucosa from Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 27470712
- PMCID: PMC5012512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.07.001
Collaborative Interferon-γ and Interleukin-17 Signaling Protects the Oral Mucosa from Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
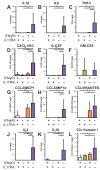
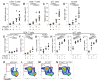
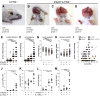
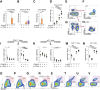
Infections with Staphylococcus aureus are a continuing and growing problem in community and hospital settings. Preclinical animal modeling of S. aureus relies on experimental infection, which carries some limitations. We describe here a novel, spontaneous model of oral staphylococcal infection in double knockout mice, deficient in the receptors for IL-17 (IL-17RA) and interferon (IFN)-γ (IFNγRI), beginning at 6 to 8 weeks of age. IFNγRI(-/-)IL17RA(-/-) (GRAKO) mice developed progressive oral abscesses. Cytometric methods revealed extensive neutrophilic infiltration of oral tissues in GRAKO mice; further investigation evidenced that IL-17 predominated neutrophil defects in these mice. To investigate the contribution of IFN-γ signaling to this native host defense to S. aureus, we observed perturbations of monocyte recruitment and macrophage differentiation in the oral tissues of GRAKO mice, and CXCL9/chemokine ligand receptor (CXCR)3-driven recruitment of T-cell oral tissues and draining lymph nodes. To address the former finding, we depleted macrophages and monocytes in vivo from IL17RA(-/-) mice using liposomes loaded with clodronate. This treatment elicited oral abscesses, recapitulating the phenotype of GRAKO mice. From these findings, we propose novel collaborative functions of IL-17 and IFN-γ, acting through neutrophils and macrophages, respectively, in native mucocutaneous host defenses to S. aureus.
Copyright © 2016 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
This Month in AJP.Am J Pathol. 2016 Sep;186(9):2237. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.05.022. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27459941
Similar articles
-
Clonally expanded γδ T cells protect against Staphylococcus aureus skin reinfection.J Clin Invest. 2018 Mar 1;128(3):1026-1042. doi: 10.1172/JCI96481. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29400698 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-gamma regulated chemokine production determines the outcome of Staphylococcus aureus infection.J Immunol. 2008 Jul 15;181(2):1323-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.2.1323. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18606687
-
IFN-gamma plays a detrimental role in murine defense against nasal colonization of Staphylococcus aureus.Immunol Lett. 2009 Apr 27;123(2):185-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.03.003. Epub 2009 Mar 19. Immunol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19428568
-
Forkhead Box O1 Regulates Macrophage Polarization Following Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Experimental Murine Data and Review of the Literature.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Dec;51(3):353-369. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8531-1. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26924010 Review.
-
Role of cytokines in host defense against Staphylococcus aureus skin infection.Histol Histopathol. 2017 Aug;32(8):761-766. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-867. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Histol Histopathol. 2017. PMID: 28078661 Review.
Cited by
-
Clonally expanded γδ T cells protect against Staphylococcus aureus skin reinfection.J Clin Invest. 2018 Mar 1;128(3):1026-1042. doi: 10.1172/JCI96481. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29400698 Free PMC article.
-
Group 1 CD1-restricted T cells contribute to control of systemic Staphylococcus aureus infection.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Apr 28;16(4):e1008443. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008443. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32343740 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 17A as a good predictor of the severity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 11;7(1):12934. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13292-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29021577 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 17 is a chief orchestrator of immunity.Nat Immunol. 2017 May 18;18(6):612-621. doi: 10.1038/ni.3742. Nat Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28518156 Review.
-
Immune Response to Persistent Staphyloccocus Aureus Periprosthetic Joint Infection in a Mouse Tibial Implant Model.J Bone Miner Res. 2022 Mar;37(3):577-594. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4489. Epub 2022 Jan 3. J Bone Miner Res. 2022. PMID: 34897801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barin J.G., Baldeviano G.C., Talor M.V., Wu L., Ong S., Fairweather D., Bedja D., Stickel N.R., Fontes J.A., Cardamone A.B., Zheng D., Gabrielson K.L., Rose N.R., Cihakova D. Fatal eosinophilic myocarditis develops in the absence of IFN-gamma and IL-17A. J Immunol. 2013;191:4038–4047. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lowy F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:520–532. - PubMed
-
- Cho J.S., Pietras E.M., Garcia N.C., Ramos R.I., Farzam D.M., Monroe H.R., Magorien J.E., Blauvelt A., Kolls J.K., Cheung A.L., Cheng G., Modlin R.L., Miller L.S. IL-17 is essential for host defense against cutaneous Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:1762–1773. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

