If Only my Leader Would just Do Something! Passive Leadership Undermines Employee Well-being Through Role Stressors and Psychological Resource Depletion
- PMID: 27470980
- PMCID: PMC5791740
- DOI: 10.1002/smi.2697
If Only my Leader Would just Do Something! Passive Leadership Undermines Employee Well-being Through Role Stressors and Psychological Resource Depletion
Abstract
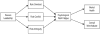
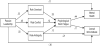
The goal of this study was to develop and test a sequential mediational model explaining the negative relationship of passive leadership to employee well-being. Based on role stress theory, we posit that passive leadership will predict higher levels of role ambiguity, role conflict and role overload. Invoking Conservation of Resources theory, we further hypothesize that these role stressors will indirectly and negatively influence two aspects of employee well-being, namely overall mental health and overall work attitude, through psychological work fatigue. Using a probability sample of 2467 US workers, structural equation modelling supported the model by showing that role stressors and psychological work fatigue partially mediated the negative relationship between passive leadership and both aspects of employee well-being. The hypothesized, sequential indirect relationships explained 47.9% of the overall relationship between passive leadership and mental health and 26.6% of the overall relationship between passive leadership and overall work attitude. Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Keywords: Conservation of Resources theory; laissez-faire leadership; mental health; passive leadership; psychological work fatigue; role stressors.
Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Aasland MS, Skogstad A, Notelaers G, Nielsen MB, Einarsen S. The prevalence of destructive leadership behavior. British Journal of Management. 2010;21:438–452.
-
- Alarcan GM. A meta-analysis of burnout with job demands, resources, and attitudes. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2011;79:549–562.
-
- Arnold KA, Turner N, Barling J, Kelloway EK, McKee M. Transformational leadership and psychological well-being: The mediating role of meaningful work. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology. 2007;12:193–203. - PubMed
-
- Asparouhov T. Sampling weights in latent variable modeling. Structural Equation Modeling. 2005;12:411–434.
-
- Asparouhov T, Muthen B. Robust chi square difference testing with mean and variance adjusted test statistics. Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén; 2006. Mplus web notes No. 10. http://www.statmodel.com/download/webnotes/webnote10.pdf.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

