Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases covalently modify strand break termini in DNA fragments in vitro
- PMID: 27471034
- PMCID: PMC5100588
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw675
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases covalently modify strand break termini in DNA fragments in vitro
Abstract
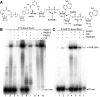
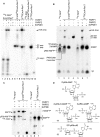
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs/ARTDs) use nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to catalyse the synthesis of a long branched poly(ADP-ribose) polymer (PAR) attached to the acceptor amino acid residues of nuclear proteins. PARPs act on single- and double-stranded DNA breaks by recruiting DNA repair factors. Here, in in vitro biochemical experiments, we found that the mammalian PARP1 and PARP2 proteins can directly ADP-ribosylate the termini of DNA oligonucleotides. PARP1 preferentially catalysed covalent attachment of ADP-ribose units to the ends of recessed DNA duplexes containing 3'-cordycepin, 5'- and 3'-phosphate and also to 5'-phosphate of a single-stranded oligonucleotide. PARP2 preferentially ADP-ribosylated the nicked/gapped DNA duplexes containing 5'-phosphate at the double-stranded termini. PAR glycohydrolase (PARG) restored native DNA structure by hydrolysing PAR-DNA adducts generated by PARP1 and PARP2. Biochemical and mass spectrometry analyses of the adducts suggested that PARPs utilise DNA termini as an alternative to 2'-hydroxyl of ADP-ribose and protein acceptor residues to catalyse PAR chain initiation either via the 2',1″-O-glycosidic ribose-ribose bond or via phosphodiester bond formation between C1' of ADP-ribose and the phosphate of a terminal deoxyribonucleotide. This new type of post-replicative modification of DNA provides novel insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying biological phenomena of ADP-ribosylation mediated by PARPs.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerases 1 and 2 Modify DNA by ADP-Ribosylating Terminal Phosphate Residues.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 26;8:606596. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.606596. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33324653 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase activities of PARP2 and PARP3: new insights into DNA ADP-ribosylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Mar 16;46(5):2417-2431. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1318. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29361132 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insight into the role of Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in DNA topology modulation and response to DNA damage.Mutagenesis. 2020 Feb 13;35(1):107-118. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gez045. Mutagenesis. 2020. PMID: 31782485 Review.
-
Insight into DNA substrate specificity of PARP1-catalysed DNA poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;10(1):3699. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60631-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32111879 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose): PARadigms and PARadoxes.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1046-65. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.010. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23290998 Review.
Cited by
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) in Condensates: The PARtnership of Phase Separation and Site-Specific Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 15;23(22):14075. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214075. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of patient-derived organoids and a characterization based drug discovery platform for treatment of gastric cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Aug 14;24(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03460-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39143546 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-ribosylation: from molecular mechanisms to human disease.Genet Mol Biol. 2019 Dec 13;43(1 suppl 1):e20190075. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0075. eCollection 2019. Genet Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31930280 Free PMC article.
-
Research Advances in the Role of the Poly ADP Ribose Polymerase Family in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 16;11:790967. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.790967. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34976832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversible mono-ADP-ribosylation of DNA breaks.FEBS J. 2017 Dec;284(23):4002-4016. doi: 10.1111/febs.14297. Epub 2017 Nov 8. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 29054115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schreiber V., Dantzer F., Ame J.C., de Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006;7:517–528. - PubMed
-
- Kim M.Y., Zhang T., Kraus W.L. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP-1: ‘PAR-laying’ NAD+ into a nuclear signal. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1951–1967. - PubMed
-
- Hottiger M.O., Hassa P.O., Luscher B., Schuler H., Koch-Nolte F. Toward a unified nomenclature for mammalian ADP-ribosyltransferases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010;35:208–219. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

