Comparisons of Portable Sleep Monitors of Different Modalities: Potential as Naturalistic Sleep Recorders
- PMID: 27471489
- PMCID: PMC4946159
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00110
Comparisons of Portable Sleep Monitors of Different Modalities: Potential as Naturalistic Sleep Recorders
Abstract
Background: Humans spend more than one-fourth of their life sleeping, and sleep quality has been significantly linked to health. However, the objective examination of ambulatory sleep quality remains a challenge, since sleep is a state of unconsciousness, which limits the reliability of self-reports. Therefore, a non-invasive, continuous, and objective method for the recording and analysis of naturalistic sleep is required.
Objective: Portable sleep recording devices provide a suitable solution for the ambulatory analysis of sleep quality. In this study, the performance of two activity-based sleep monitors (Actiwatch and MTN-210) and a single-channel electroencephalography (EEG)-based sleep monitor (SleepScope) were compared in order to examine their reliability for the assessment of sleep quality.
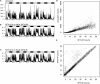
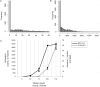
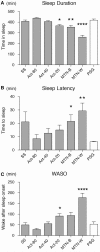
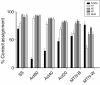
Methods: Twenty healthy adults were recruited for this study. First, data from daily activity recorded by Actiwatch and MTN-210 were compared to determine whether MTN-210, a more affordable device, could yield data similar to Actiwatch, the de facto standard. In addition, sleep detection ability was examined using data obtained by polysomnography as reference. One simple analysis included comparing the sleep/wake detection ability of Actiwatch, MTN-210, and SleepScope. Furthermore, the fidelity of sleep stage determination was examined using SleepScope in finer time resolution.
Results: The results indicate that MTN-210 demonstrates an activity pattern comparable to that of Actiwatch, although their sensitivity preferences were not identical. Moreover, MTN-210 provides assessment of sleep duration comparable to that of the wrist-worn Actiwatch when MTN-210 was attached to the body. SleepScope featured superior overall sleep detection performance among the three methods tested. Furthermore, SleepScope was able to provide information regarding sleep architecture, although systemic bias was found.
Conclusion: The present results suggest that single-channel EEG-based sleep monitors are the superior option for the examination of naturalistic sleep. The current results pave a possible future use for reliable portable sleep assessment methods in an ambulatory rather than a laboratory setting.
Keywords: activity recorders; polysomnography; portable sleep monitors; single channel EEG; sleep estimation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Feasibility and Utility of Continuous Sleep Monitoring in Critically Ill Patients Using a Portable Electroencephalography Monitor.Anesth Analg. 2016 Jul;123(1):206-12. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001330. Anesth Analg. 2016. PMID: 27159066 Free PMC article.
-
Exploratory Validation of Sleep-Tracking Devices in Patients with Psychiatric Disorders.Nat Sci Sleep. 2023 Apr 24;15:301-312. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S400944. eCollection 2023. Nat Sci Sleep. 2023. PMID: 37123093 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Sleep Quality Assessment Using Wearable Sensors by Including Information From Postural/Sleep Position Changes and Body Acceleration: A Comparison of Chest-Worn Sensors, Wrist Actigraphy, and Polysomnography.J Clin Sleep Med. 2017 Nov 15;13(11):1301-1310. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6802. J Clin Sleep Med. 2017. PMID: 28992827 Free PMC article.
-
State of home sleep studies.Clin Chest Med. 2003 Jun;24(2):283-95. doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(03)00018-2. Clin Chest Med. 2003. PMID: 12800784 Review.
-
Home assessment of sleep disorders by portable monitoring.J Clin Neurophysiol. 1996 Jul;13(4):272-84. doi: 10.1097/00004691-199607000-00002. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8858490 Review.
Cited by
-
Work Habit-Related Sleep Debt; Insights From Factor Identification Analysis of Actigraphy Data.Front Public Health. 2021 Mar 10;9:630640. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.630640. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33777884 Free PMC article.
-
A Machine Learning Model for Predicting Sleep and Wakefulness Based on Accelerometry, Skin Temperature and Contextual Information.Nat Sci Sleep. 2024 Jun 6;16:699-710. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S452799. eCollection 2024. Nat Sci Sleep. 2024. PMID: 38863481 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Workday/Leisure Day Lifestyle Behavior and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Among Night Shift Workers Using the Isotemporal Substitution Model.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;13(8):908. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13080908. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281857 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of Actigraphy in Measurement of Sleep in Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes.J Clin Sleep Med. 2017 May 15;13(5):669-674. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6580. J Clin Sleep Med. 2017. PMID: 28162146 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of taking a nap or break immediately after night shift on nurses' fatigue recovery and sleep episodes: a quasi-experimental study.J Physiol Anthropol. 2025 Jul 15;44(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40101-025-00399-2. J Physiol Anthropol. 2025. PMID: 40665465 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

