The immune network in thyroid cancer
- PMID: 27471646
- PMCID: PMC4938375
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1168556
The immune network in thyroid cancer
Abstract
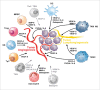
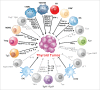
The immune system plays critical roles in tumor prevention, but also in its initiation and progression. Tumors are subjected to immunosurveillance, but cancer cells generate an immunosuppressive microenvironment that favors their escape from immune-mediated elimination. During chronic inflammation, immune cells can contribute to the formation and progression of tumors by producing mitogenic, prosurvival, proangiogenic and lymphangiogenic factors. Thyroid cancer is the most frequent type of endocrine neoplasia and is the most rapidly increasing cancer in the US. In this review, we discuss recent findings on how different immune cells and mediators can contribute to thyroid cancer development and progression.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; CXCL8/IL-8; T reg cells; chemokines; dendritic cells; lymphangiogenesis; macrophages; mast cells; neutrophils; thyroid cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008; 454:436-44; PMID:18650914; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nature07205 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zitvogel L, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Andre F, Tesniere A, Kroemer G. The anticancer immune response: indispensable for therapeutic success? J Clin Invest 2008; 118:1991-2001; PMID:18523649; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1172/JCI35180 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature 2001; 410:1107-11; PMID:11323675; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/35074122 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cunha LL, Marcello MA, Ward LS. The role of the inflammatory microenvironment in thyroid carcinogenesis. Endocrine-related cancer 2014; 21:R85-R103; PMID:24302667; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1530/ERC-13-0431 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carling T, Udelsman R. Thyroid cancer. Ann Rev Med 2014; 65:125-37; PMID:24274180; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev-med-061512-105739 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
