In Vivo and In Vitro Genotoxic and Epigenetic Effects of Two Types of Cola Beverages and Caffeine: A Multiassay Approach
- PMID: 27471731
- PMCID: PMC4947684
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/7574843
In Vivo and In Vitro Genotoxic and Epigenetic Effects of Two Types of Cola Beverages and Caffeine: A Multiassay Approach
Abstract
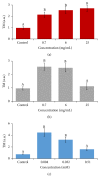
The aim of this work was to assess the biological and food safety of two different beverages: Classic Coca Cola™ (CCC) and Caffeine-Free Coca Cola (CFCC). To this end, we determined the genotoxicological and biological effects of different doses of lyophilised CCC and CFCC and Caffeine (CAF), the main distinctive constituent. Their toxic/antitoxic, genotoxic/antigenotoxic, and chronic toxicity (lifespan assay) effects were determined in vivo using the Drosophila model. Their cytotoxic activities were determined using the HL-60 in vitro cancer model. In addition, clastogenic DNA toxicity was measured using internucleosomal fragmentation and SCGE assays. Their epigenetic effects were assessed on the HL-60 methylation status using some repetitive elements. The experimental results showed a slight chemopreventive effect of the two cola beverages against HL-60 leukaemia cells, probably mediated by nonapoptotic mechanisms. Finally, CCC and CAF induced a global genome hypomethylation evaluated in LINE-1 and Alu M1 repetitive elements. Overall, we demonstrated for the first time the safety of this famous beverage in in vivo and in vitro models.
Figures




References
-
- Wildman R. Handbook of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods. Boca Raton, Fla, USA: CRC Press; 2001. Nutraceuticals: a brief review of historical and teleological aspects; pp. 2–12.
-
- Merinas-Amo M. T., Villalba-Benito L., Almagro-Berlanga R., et al. Toxicological, genotoxicological, antigenotoxicological, cytotoxicity and lifespan studies of beer and some components. Toxicology Letters. 2013;221:p. S124. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.05.223. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

