House dust mite sublingual tablet is effective and safe in patients with allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 27471838
- PMCID: PMC5324568
- DOI: 10.1111/all.12996
House dust mite sublingual tablet is effective and safe in patients with allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: House dust mite (HDM) is the major indoor allergen for allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis (AR) and asthma. Although sublingual immunotherapy is a curative treatment for HDM-induced AR, data from large-scale studies are limited. We evaluated the efficacy and safety of HDM tablets in adolescent and adult patients (aged 12-64 years) with HDM-induced AR with or without intermittent asthma.
Methods: In a double-blind trial in Japan, 968 subjects were randomized 1 : 1 : 1 to 300 index of reactivity (IR), 500 IR, or placebo groups. The primary endpoint was the Average Adjusted Symptom Score (AASS) in the last eight weeks of the 52-week treatment. Secondary endpoints included individual nasal and ocular symptom scores, rescue medication use, and the Japanese Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire (JRQLQ) scores.
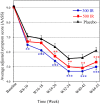
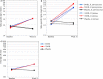
Results: The AASS in the last eight weeks of treatment significantly improved in both the 300 IR and the 500 IR groups compared to that in the placebo group (P < 0.001). In the 300 IR group, the onset of action occurred at week 8-10. All four nasal symptoms significantly improved in both active treatment groups; rescue medication use and JRQLQ outcome improved in the 300 IR group. Most adverse events (AEs) were mild, and 16 serious AEs (SAEs) were reported; however, none of them were drug-related.
Conclusions: One-year treatment with 300 IR and 500 IR HDM tablets was effective without major safety concerns. The recommended therapeutic dose for AR is 300 IR.
Keywords: Average Adjusted Symptom Score; allergic rhinitis; clinical study; house dust mite; sublingual immunotherapy tablet.
© 2016 The Authors. Allergy Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of the SQ house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet in Japanese adults and adolescents with house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Jun;139(6):1840-1848.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.043. Epub 2016 Nov 15. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27864024 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of house dust mite sublingual tablet in the treatment of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis: A randomized trial in a pediatric population.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2019 Feb;30(1):66-73. doi: 10.1111/pai.12984. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30281866 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet in North American adolescents and adults in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Dec;138(6):1631-1638. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.06.044. Epub 2016 Aug 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27521719 Clinical Trial.
-
300 IR HDM tablet: a sublingual immunotherapy tablet for the treatment of house dust mite-associated allergic rhinitis.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016 Nov;12(11):1141-1151. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2016.1237288. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27632814 Review.
-
House dust mite sublingual immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis.Immunotherapy. 2018 Jun;10(7):567-578. doi: 10.2217/imt-2018-0013. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Immunotherapy. 2018. PMID: 29562802 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulated expression of substance P and NK1R in blood monocytes and B cells of patients with allergic rhinitis and asthma.Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 Oct 21;210(1):39-52. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac074. Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36001730 Free PMC article.
-
Guideline on allergen immunotherapy in IgE-mediated allergic diseases: S2K Guideline of the German Society of Allergology and Clinical Immunology (DGAKI), Society of Pediatric Allergology and Environmental Medicine (GPA), Medical Association of German Allergologists (AeDA), Austrian Society of Allergology and Immunology (ÖGAI), Swiss Society for Allergology and Immunology (SSAI), German Dermatological Society (DDG), German Society of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (DGHNO-KHC), German Society of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine (DGKJ), Society of Pediatric Pulmonology (GPP), German Respiratory Society (DGP), German Professional Association of Otolaryngologists (BVHNO), German Association of Paediatric and Adolescent Care Specialists (BVKJ), Federal Association of Pneumologists, Sleep and Respiratory Physicians (BdP), Professional Association of German Dermatologists (BVDD).Allergol Select. 2022 Sep 6;6:167-232. doi: 10.5414/ALX02331E. eCollection 2022. Allergol Select. 2022. PMID: 36178453 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Long-term Efficacy of Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Pediatric and Adult Patients With Allergic Rhinitis.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019 Jan;11(1):68-78. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.1.68. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 30479078 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of dual sublingual immunotherapy with Japanese cedar pollen and house dust mite allergens in patients with allergic rhinitis sensitized to multiple allergens.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022 Jan 21;7(1):36-42. doi: 10.1002/lio2.740. eCollection 2022 Feb. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35155781 Free PMC article.
-
[Adjuvants].Hautarzt. 2017 Apr;68(4):292-296. doi: 10.1007/s00105-017-3935-2. Hautarzt. 2017. PMID: 28130604 Review. German.
References
-
- Calderón MA, Linneberg A, Kleine‐Tebbe J, De Blay F, Hernandez Fernandez de Rojas D, Virchow JC et al. Respiratory allergy caused by house dust mites: what do we really know? J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;13:38–48. - PubMed
-
- Calderon MA, Casale TB, Nelson HS, Demoly P. An evidence‐based analysis of house dust mite allergen immunotherapy: a call for more rigorous clinical studies. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013;132:1322–1336. - PubMed
-
- Calderón MA, Kleine‐Tebbe J, Linneberg A, De Blay F, Hernandez Fernandez de Rojas D, Virchow JC. House dust mite respiratory allergy: an overview of current therapeutic strategies. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2015;3:843–855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

