Circulating Levels of Irisin in Hypopituitary and Normal Subjects
- PMID: 27472279
- PMCID: PMC4966893
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160364
Circulating Levels of Irisin in Hypopituitary and Normal Subjects
Abstract
Context: The recently identified myokine irisin conveys some of the benefits of exercise. Hypopituitarism with adult growth hormone deficiency (HP) is a situation characterized by decreased GH secretion and an altered body composition.
Objective: Our aim was to study the skeletal muscle hormone irisin in HP, and compare the results with a similar group of normal subjects.
Participants and methods: Seventeen HP patients and fifty-one normal subjects of similar age and sex were studied. The diagnosis of GH deficiency was confirmed by the presence of pituitary disease and a peak GH secretion below 3 μg/L after an insulin tolerance test. The patients were adequately treated for all pituitary hormone deficits, except for GH. Fasting serum irisin was measured with an enzyme immunoassay, and HOMA-IR, QUICKI and HOMA-β were calculated.
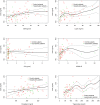
Results: Fasting irisin levels (ng/ml) were similar in normal [208.42 (168.44-249.23)] and HP patients [195.13 (178.44-241.44)]. In the control group there were moderate significant positive correlations between irisin and BMI, waist circumference, leptin, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, HOMA-β, triglycerides, and cholesterol. In the control group there were moderate significant negative correlations between irisin and IGF-I and QUICKI. In the hypopituitary group there were moderate significant positive correlations between irisin and body fat and HOMA-β.
Conclusions: We found similar irisin levels in GH deficiency hypopituitary patients when compared with normal subjects. The correlation between irisin and adiposity related factors suggests that that in the case of this clinical model, irisin is regulated by adiposity and not by GH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Anastasilakis AD, Polyzos SA, Saridakis ZG, Kynigopoulos G, Skouvaklidou EC, Molyvas D, et al. Circulating irisin in healthy, young individuals: day-night rhythm, effects of food intake and exercise, and associations with gender, physical activity, diet, and body composition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(9):3247–55. Epub 2014/06/11. 10.1210/jc.2014-1367 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huh JY, Panagiotou G, Mougios V, Brinkoetter M, Vamvini MT, Schneider BE, et al. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism. 2012;61(12):1725–38. Epub 2012/09/29. S0026-0495(12)00332-0 [pii] 10.1016/j.metabol.2012.09.002 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crujeiras AB, Pardo M, Arturo RR, Navas-Carretero S, Zulet MA, Martinez JA, et al. Longitudinal variation of circulating irisin after an energy restriction-induced weight loss and following weight regain in obese men and women. Am J Hum Biol. 2014;26(2):198–207. Epub 2014/01/01. 10.1002/ajhb.22493 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous