Parenchymal lung involvement in adult-onset Still disease: A STROBE-compliant case series and literature review
- PMID: 27472698
- PMCID: PMC5265835
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004258
Parenchymal lung involvement in adult-onset Still disease: A STROBE-compliant case series and literature review
Abstract
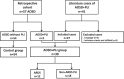
Parenchymal lung involvement (PLI) in adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) has seldom, if ever, been studied. We examine here retrospective cohort AOSD cases and present a review of the literature (1971-2014) on AOSD-related PLI cases.Patients with PLI were identified in 57 AOSD cases. For inclusion, the patients had to fulfill Yamaguchi or Fautrel classification criteria, show respiratory symptoms, and have imaging evidence of pulmonary involvement, and data allowing exclusion of infectious, cardiogenic, toxic, or iatrogenic cause of PLI should be available. This AOSD + PLI group was compared with a control group (non-PLI-complicated AOSD cases from the same cohort).AOSD + PLI was found in 3 out of the 57 patients with AOSD (5.3%) and the literature mentioned 27 patients. Among these 30 AOSD + PLI cases, 12 presented an acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and the remaining 18 another PLI. In the latter, a nonspecific interstitial pneumonia computed tomography pattern prevailed in the lower lobes, pulmonary function tests showed a restrictive lung function, the alveolar differential cell count was neutrophilic in half of the cases, and the histological findings were consistent with bronchiolitis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Corticosteroids were fully efficient in all but 3 patients. Ten out of 12 ARDS cases occurred during the first year of the disease course. All ARDS-complicated AOSD cases received corticosteroids with favorable outcomes in 10 (2 deceased). Most PLIs occurred during the systemic onset of AOSD.PLI may occur in 5% of AOSDs, of which ARDS is the most severe. Very often, corticosteroids are efficient in controlling this complication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Narula N, Narula T, Abril A. Seizing the clinical presentation in adult onset Still's disease. An extensive literature review. Autoimmun Rev 2015; 14:472–477. - PubMed
-
- Gerfaud-Valentin M, Jamilloux Y, Iwaz J, et al. Adult-onset Still's disease. Autoimmun Rev 2014; 13:708–722. - PubMed
-
- Fautrel B, Le Moël G, Saint-Marcoux B, et al. Diagnostic value of ferritin and glycosylated ferritin in adult onset Still's disease. J Rheumatol 2001; 28:322–329. - PubMed
-
- Maria ATJ, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, et al. Adult onset Still's disease (AOSD) in the era of biologic therapies: dichotomous view for cytokine and clinical expressions. Autoimmun Rev 2014; 13:1149–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous