Health-related quality of life in Hodgkin lymphoma: a systematic review
- PMID: 27473596
- PMCID: PMC4966803
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-016-0515-6
Health-related quality of life in Hodgkin lymphoma: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL) is highly curable with well-established treatment regimens; however, the impact on patient's health-related quality of life (HRQL) from diagnosis through survivorship is unclear. This systematic review aimed to describe the available literature on HRQL in HL, assess the quality of these studies, identify gaps in the literature and recommend further areas of research.
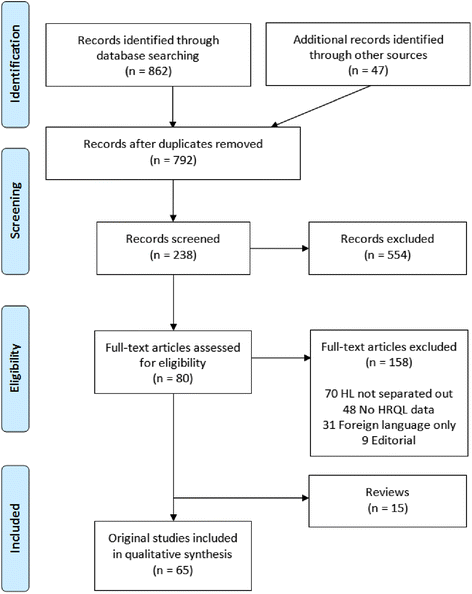
Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, we performed a systematic review to include studies assessing the HRQL in HL patients. Articles identified through database searches were screened and data extracted. Quality was evaluated using a 6-point scale, adapted from published HRQL systematic reviews.
Results: Sixty five articles published between 1986 and 2015 met inclusion criteria. These included 53 (82 %) cross-sectional studies; 12 (18 %) longitudinal studies, including three embedded in randomized trials; and three additional longitudinal studies that began assessment at diagnosis. Study sample sizes of HL patients varied considerably with only five (42 %) longitudinal studies including more than 50 patients. Multidimensional HRQL was assessed in 45 studies, single HRQL domains in 22 studies, and symptoms, including fatigue, in 28 studies.
Conclusions: The majority of studies employed a cross-sectional design, enrolling HL survivors at least 10 years after the completion of therapy. Emphasis on HRQL following therapy may inform initial treatment decisions and long-term survivorship goals. We recommend that future research include prospective, longitudinal randomized designs across both treatment and time.
Keywords: Hodgkin lymphoma; Quality of life; Survivorship; Systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Hodgkin Lymphoma. National Cancer Institute. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/hodg.html. Accessed 15 Sept 2015.
-
- American Cancer Society. What are the Key Statistics about Hodgkin Disease? 2015. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/hodgkindisease/detailedguide/hodgkin-diseas.... Accessed 15 Sept 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous