Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) blunt the response of Neuropeptide Y/Agouti-related peptide (NPY/AgRP) glucose inhibited (GI) neurons to decreased glucose
- PMID: 27473896
- PMCID: PMC5018455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.07.035
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) blunt the response of Neuropeptide Y/Agouti-related peptide (NPY/AgRP) glucose inhibited (GI) neurons to decreased glucose
Abstract
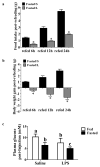
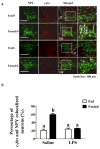
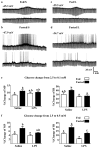
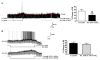
A population of Neuropeptide Y (NPY) neurons which co-express Agouti-related peptide (AgRP) in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC) are inhibited at physiological levels of brain glucose and activated when glucose levels decline (e.g. glucose-inhibited or GI neurons). Fasting enhances the activation of NPY/AgRP-GI neurons by low glucose. In the present study we tested the hypothesis that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inhibits the enhanced activation of NPY/AgRP-GI neurons by low glucose following a fast. Mice which express green fluorescent protein (GFP) on their NPY promoter were used to identify NPY/AgRP neurons. Fasting for 24h and LPS injection decreased blood glucose levels. As we have found previously, fasting increased c-fos expression in NPY/AgRP neurons and increased the activation of NPY/AgRP-GI neurons by decreased glucose. As we predicted, LPS blunted these effects of fasting at the 24h time point. Moreover, the inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) blocked the activation of NPY/AgRP-GI neurons by decreased glucose. These data suggest that LPS and TNFα may alter glucose and energy homeostasis, in part, due to changes in the glucose sensitivity of NPY/AgRP neurons. Interestingly, our findings also suggest that NPY/AgRP-GI neurons use a distinct mechanism to sense changes in extracellular glucose as compared to our previous studies of GI neurons in the adjacent ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus.
Keywords: Anorexia; Fasting; GI neurons; LPS; NPY/AgRP neurons; TNFα.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no Conflict of interest.
Figures
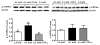

References
-
- Amitani M, Asakawa A, Amitani H, Inui A. Control of food intake and muscle wasting in cachexia. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 2013;45:2179–2185. - PubMed
-
- Anderson ST, Commins S, Moynagh PN, Coogan AN. Lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis induces long-lasting affective changes in the mouse. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2015;43:98–109. - PubMed
-
- Arruda AP, Milanski M, Romanatto T, Solon C, Coope A, Alberici LC, Festuccia WT, Hirabara SM, Ropelle E, Curi R, Carvalheira JB, Vercesi AE, Velloso LA. Hypothalamic Actions of Tumor Necrosis Factor α Provide the Thermogenic Core for the Wastage Syndrome in Cachexia. Endocrinology. 2010;151:683–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

