Influences of innate immunity, autophagy, and fibroblast activation in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis
- PMID: 27474089
- PMCID: PMC5142210
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00221.2016
Influences of innate immunity, autophagy, and fibroblast activation in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis
Abstract
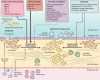
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive interstitial lung disease characterized by accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) and impaired gas exchange. The pathobiological mechanisms that account for disease progression are poorly understood but likely involve alterations in innate inflammatory cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts. Thus we seek to review the most recent literature highlighting the complex roles of neutrophils and macrophages as both promoters of fibrosis and defenders against infection. With respect to epithelial cells and fibroblasts, we review the data suggesting that defective autophagy promotes the fibrogenic potential of both cell types and discuss new evidence related to matrix metalloproteinases, growth factors, and cellular metabolism in the form of lactic acid generation that may have consequences for promoting fibrogenesis. We discuss potential cross talk between innate and structural cell types and also highlight literature that may help explain the limitations of current IPF therapies.
Keywords: epithelial cells; fibroblasts; fibrosis; innate immunity; lung.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Ahuja S, Knudsen L, Chillappagari S, Henneke I, Ruppert C, Korfei M, Gochuico BR, Bellusci S, Seeger W, Ochs M, Guenther A, Mahavadi P. MAP1LC3B overexpression protects against Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type-1 induced defective autophagy in vitro. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 310: L519–L531, 2016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anthony D, McQualter JL, Bishara M, Lim EX, Yatmaz S, Seow HJ, Hansen M, Thompson M, Hamilton JA, Irving LB, Levy BD, Vlahos R, Anderson GP, Bozinovski S. SAA drives proinflammatory heterotypic macrophage differentiation in the lung via CSF-1R-dependent signaling. FASEB J 28: 3867–3877, 2014. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

