Development of a highly sensitive real-time nested RT-PCR assay in a single closed tube for detection of enterovirus 71 in hand, foot, and mouth disease
- PMID: 27475103
- PMCID: PMC7086773
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-016-2985-6
Development of a highly sensitive real-time nested RT-PCR assay in a single closed tube for detection of enterovirus 71 in hand, foot, and mouth disease
Abstract
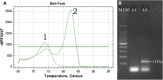
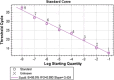
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is one of the major causative agents of outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). A commercial TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR assay has been widely used for the differential detection of EV71 despite its relatively high cost and failure to detect samples with a low viral load (Ct value > 35). In this study, a highly sensitive real-time nested RT-PCR (RTN RT-PCR) assay in a single closed tube for detection of EV71 in HFMD was developed. The sensitivity and specificity of this assay were evaluated using a reference EV71 stock and a panel of controls consisting of coxsackievirus A16 (CVA16) and common respiratory viruses, respectively. The clinical performance of this assay was evaluated and compared with those of a commercial TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) assay and a traditional two-step nested RT-PCR assay. The limit of detection for the RTN RT-PCR assay was 0.01 TCID50/ml, with a Ct value of 38.3, which was the same as that of the traditional two-step nested RT-PCR assay and approximately tenfold lower than that of the qRT-PCR assay. When testing the reference strain EV71, this assay showed favorable detection reproducibility and no obvious cross-reactivity. The testing results of 100 clinical throat swabs from HFMD-suspected patients revealed that 41 samples were positive for EV71 by both RTN RT-PCR and traditional two-step nested RT-PCR assays, whereas only 29 were EV71 positive by qRT-PCR assay.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A one-step, triplex, real-time RT-PCR assay for the simultaneous detection of enterovirus 71, coxsackie A16 and pan-enterovirus in a single tube.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 16;9(7):e102724. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102724. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25029500 Free PMC article.
-
Improved detection limit in rapid detection of human enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 by a novel reverse transcription-isothermal multiple-self-matching-initiated amplification assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Jun;52(6):1862-70. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03298-13. Epub 2014 Mar 19. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24648558 Free PMC article.
-
Development of duplex real-time RT-PCR based on Taqman technology for detecting simultaneously the genome of pan-enterovirus and enterovirus 71.J Med Virol. 2013 Jul;85(7):1274-9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23588. J Med Virol. 2013. PMID: 23918544
-
Molecular epidemiology and evolution of human enterovirus 71 and hand, foot and mouth disease.Yi Chuan. 2015 May;37(5):426-35. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.14-255. Yi Chuan. 2015. PMID: 25998430 Review.
-
A review on current diagnostic tools and potential optical absorption spectroscopy for HFMD detection.Anal Biochem. 2023 Dec 15;683:115368. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2023.115368. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Anal Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37890549 Review.
Cited by
-
Applicability of duplex real time and lateral flow strip reverse-transcription recombinase aided amplification assays for the detection of Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16.Virol J. 2019 Dec 30;16(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1264-z. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31888694 Free PMC article.
-
Various theranostics and immunization strategies based on nanotechnology against Covid-19 pandemic: An interdisciplinary view.Life Sci. 2021 Aug 1;278:119580. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119580. Epub 2021 May 12. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33991549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic value of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for hand, foot, and mouth disease.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jun;35(6):e23776. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23776. Epub 2021 Apr 1. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33792998 Free PMC article.
-
A one-step reverse-transcription recombinase aided PCR assay for the rapid and sensitive detection of human enteroviruses.Biosaf Health. 2023 Mar 11;5(2):126-131. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.03.002. eCollection 2023 Apr. Biosaf Health. 2023. PMID: 40078830 Free PMC article.
-
A multiplex one-tube nested real time RT-PCR assay for simultaneous detection of respiratory syncytial virus, human rhinovirus and human metapneumovirus.Virol J. 2018 Oct 30;15(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-1061-0. Virol J. 2018. PMID: 30376870 Free PMC article.
References
-
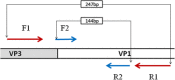
- Ge S, Yan Q, He S, Zhuang S, Niu J, Xia N. Specific primer amplification of the VP1 region directed by 5′ UTR sequence analysis: enterovirus testing and identification in clinical samples from hand-foot-and-mouth disease patients. J Virol Methods. 2013;193(2):463–469. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.06.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

