Inverse 4D conformal planning for lung SBRT using particle swarm optimization
- PMID: 27476472
- PMCID: PMC5175212
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/61/16/6181
Inverse 4D conformal planning for lung SBRT using particle swarm optimization
Abstract
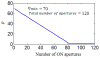
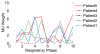
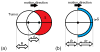
A critical aspect of highly potent regimens such as lung stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is to avoid collateral toxicity while achieving planning target volume (PTV) coverage. In this work, we describe four dimensional conformal radiotherapy using a highly parallelizable swarm intelligence-based stochastic optimization technique. Conventional lung CRT-SBRT uses a 4DCT to create an internal target volume and then, using forward-planning, generates a 3D conformal plan. In contrast, we investigate an inverse-planning strategy that uses 4DCT data to create a 4D conformal plan, which is optimized across the three spatial dimensions (3D) as well as time, as represented by the respiratory phase. The key idea is to use respiratory motion as an additional degree of freedom. We iteratively adjust fluence weights for all beam apertures across all respiratory phases considering OAR sparing, PTV coverage and delivery efficiency. To demonstrate proof-of-concept, five non-small-cell lung cancer SBRT patients were retrospectively studied. The 4D optimized plans achieved PTV coverage comparable to the corresponding clinically delivered plans while showing significantly superior OAR sparing ranging from 26% to 83% for D max heart, 10%-41% for D max esophagus, 31%-68% for D max spinal cord and 7%-32% for V 13 lung.
Figures









References
-
- Coolens C, Evans PM, Seco J, Webb S, Blackall JM, Rietzel E, Chen GT. The susceptibility of IMRT dose distributions to intrafraction organ motion: an investigation into smoothing filters derived from four dimensional computed tomography data. Med Phys. 2006 Aug;33(8):2809–18. - PubMed
-
- Rietzel E, Chen GT, Choi NC, Willet CG. Four-dimensional image-based treatment planning: Target volume segmentation and dose calculation in the presence of respiratory motion. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Apr 1;61(5):1535–50. - PubMed
-
- Nioutsikou E, Richard NSTJ, Bedford JL, Webb S. Quantifying the effect of respiratory motion on lung tumour dosimetry with the aid of a breathing phantom with deforming lungs. Phys Med Biol. 2006 Jul 21;51(14):3359–74. - PubMed
-
- Mutaf YD, Scicutella CJ, Michalski D, Fallon K, Brandner ED, Bednarz G, Huq MS. A simulation study of irregular respiratory motion and its dosimetric impact on lung tumors. Phys Med Biol. 2011 Feb 7;56(3):845–59. - PubMed
-
- Keall PJ, et al. The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76. Med Phys. 2006 Oct;33(10):3874–900. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
