Disentangling the Role of Astrocytes in Alcohol Use Disorder
- PMID: 27476876
- PMCID: PMC5407469
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13168
Disentangling the Role of Astrocytes in Alcohol Use Disorder
Abstract
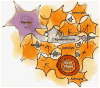
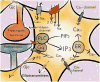
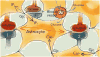
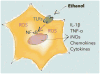
Several laboratories recently identified that astrocytes are critical regulators of addiction machinery. It is now known that astrocyte pathology is a common feature of ethanol (EtOH) exposure in both humans and animal models, as even brief EtOH exposure is sufficient to elicit long-lasting perturbations in astrocyte gene expression, activity, and proliferation. Astrocytes were also recently shown to modulate the motivational properties of EtOH and other strongly reinforcing stimuli. Given the role of astrocytes in regulating glutamate homeostasis, a crucial component of alcohol use disorder (AUD), astrocytes might be an important target for the development of next-generation alcoholism treatments. This review will outline some of the more prominent features displayed by astrocytes, how these properties are influenced by acute and long-term EtOH exposure, and future directions that may help to disentangle astrocytic from neuronal functions in the etiology of AUD.
Keywords: Alcohol Use Disorder; Astrocyte; Gliotransmission; Glutamate.
Copyright © 2016 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing or conflicting interests to declare.
Figures



Comment in
-
Disruption of Integrated Neuronal and Astrocytic Signaling Contributes to Alcohol Use Disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Nov;40(11):2309-2311. doi: 10.1111/acer.13227. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 27716954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adermark L, Clarke RB, Olsson T, Hansson E, Soderpalm B, Ericson M. Implications for glycine receptors and astrocytes in ethanol-induced elevation of dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. Addict Biol. 2011a;16:43–54. - PubMed
-
- Adermark L, Clarke RB, Soderpalm B, Ericson M. Ethanol-induced modulation of synaptic output from the dorsolateral striatum in rat is regulated by cholinergic interneurons. Neurochem Int. 2011b;58:693–699. - PubMed
-
- Adermark L, Jonsson S, Ericson M, Soderpalm B. Intermittent ethanol consumption depresses endocannabinoid-signaling in the dorsolateral striatum of rat. Neuropharmacology. 2011c;61:1160–1165. - PubMed
-
- Adermark L, Jonsson S, Soderpalm B, Ericson M. Region-specific depression of striatal activity in Wistar rat by modest ethanol consumption over a ten-month period. Alcohol. 2013;47:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Adermark L, Lovinger DM. Ethanol effects on electrophysiological properties of astrocytes in striatal brain slices. Neuropharmacology. 2006;51:1099–1108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

