Noninvasive Facial Rejuvenation. Part 2: Physician-Directed-Neuromodulators and Fillers
- PMID: 27478422
- PMCID: PMC4961509
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1584819
Noninvasive Facial Rejuvenation. Part 2: Physician-Directed-Neuromodulators and Fillers
Abstract
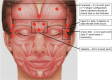
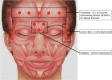
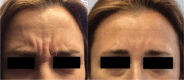
A proper knowledge of noninvasive facial rejuvenation is integral to the practice of a cosmetic surgeon. Noninvasive facial rejuvenation can be divided into patient- versus physician-directed modalities. Patient-directed facial rejuvenation combines the use of facial products such as sunscreen, moisturizers, retinoids, α-hydroxy acids, and various antioxidants to both maintain youthful skin as well as rejuvenate damaged skin. Physicians may recommend and often prescribe certain products, but patients are in control with this type of facial rejuvenation. On the other hand, physician-directed facial rejuvenation entails modalities that require direct physician involvement, such as neuromodulators, filler injections, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, and chemical peels. With the successful integration of each of these modalities, a complete facial regimen can be established and patient satisfaction can be maximized. This article is the second in a three-part series describing noninvasive facial rejuvenation. Here the authors discuss neuromodulators and fillers in detail, focusing on indications for use, techniques, and common side effects.
Keywords: fillers; neuromodulators; noninvasive facial rejuvenation.
Figures


References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. 2015 Cosmetic Plastic Surgery Statistics. 2015 Available at: http://www.plasticsurgery.org/Documents/news-resources/statistics/2015-s.... Accessed February 15, 2016
-
- Carruthers A, Sadick N, Brandt F. et al.Evolution of facial aesthetic treatment over five or more years: a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of continuous onabotulinumtoxinA treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41(6):693–701. - PubMed
-
- Matarasso S L Comparison of botulinum toxin types A and B: a bilateral and double-blind randomized evaluation in the treatment of canthal rhytides Dermatol Surg 20032917–13., discussion 13 - PubMed
-
- Carruthers J, Carruthers A. Botulinum toxin A in the mid and lower face and neck. Dermatol Clin. 2004;22(2):151–158. - PubMed
-
- Allen S B, Goldenberg N A. Pain difference associated with injection of abobotulinumtoxinA reconstituted with preserved saline and preservative-free saline: a prospective, randomized, side-by-side, double-blind study. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38(6):867–870. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

