Spectral Analysis of Chinese Medicinal Herbs Based on Delayed Luminescence
- PMID: 27478482
- PMCID: PMC4958485
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8469024
Spectral Analysis of Chinese Medicinal Herbs Based on Delayed Luminescence
Abstract
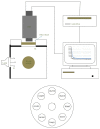
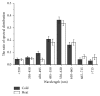
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) plays a critical role in healthcare; however, it lacks scientific evidence to support the multidimensional therapeutic effects. These effects are based on experience, and, to date, there is no advanced tool to evaluate these experience based effects. In the current study, Chinese herbal materials classified with different cold and heat therapeutic properties, based on Chinese medicine principles, were investigated using spectral distribution, as well as the decay probability distribution based on delayed luminescence (DL). A detection system based on ultraweak biophoton emission was developed to determine the DL decay kinetics of the cold and heat properties of Chinese herbal materials. We constructed a mathematical model to fit the experimental data and characterize the properties of Chinese medicinal herbs with different parameters. The results demonstrated that this method has good reproducibility. Moreover, there is a significant difference (p < 0.05) in the spectral distribution and the decay probability distribution of Chinese herbal materials with cold and heat properties. This approach takes advantage of the comprehensive nature of DL compared with more reductionist approaches and is more consistent with TCM principles, in which the core comprises holistic views.
Figures


References
-
- Gao X. Science of Chinese Materia Medica. Beijing, China: Publishing House of China of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2007.
-
- Nie B., Du J., Xu G., et al. Classification and discrimination for traditional Chinese medicine nature based on OSC-OPLS/O2PLS-DA. Proceedings of the International Forum on Information Technology and Applications (IFITA '10); July 2010; Kunming, China. pp. 354–357. - DOI
-
- Feng S., Liu Y., Wang X., et al. Application of multivariate statistical analysis in correlation between GC-MS chromatograms of polysaccharide hydrolysis composition acetylation and cold-heat nature of traditional Chinese medicine. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae. 2013;9:143–146.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

