Identification of polymorphic SVA retrotransposons using a mobile element scanning method for SVA (ME-Scan-SVA)
- PMID: 27478512
- PMCID: PMC4967303
- DOI: 10.1186/s13100-016-0072-x
Identification of polymorphic SVA retrotransposons using a mobile element scanning method for SVA (ME-Scan-SVA)
Abstract
Background: Mobile element insertions are a major source of human genomic variation. SVA (SINE-R/VNTR/Alu) is the youngest retrotransposon family in the human genome and a number of diseases are known to be caused by SVA insertions. However, inter-individual genomic variations generated by SVA insertions and their impacts have not been studied extensively due to the difficulty in identifying polymorphic SVA insertions.
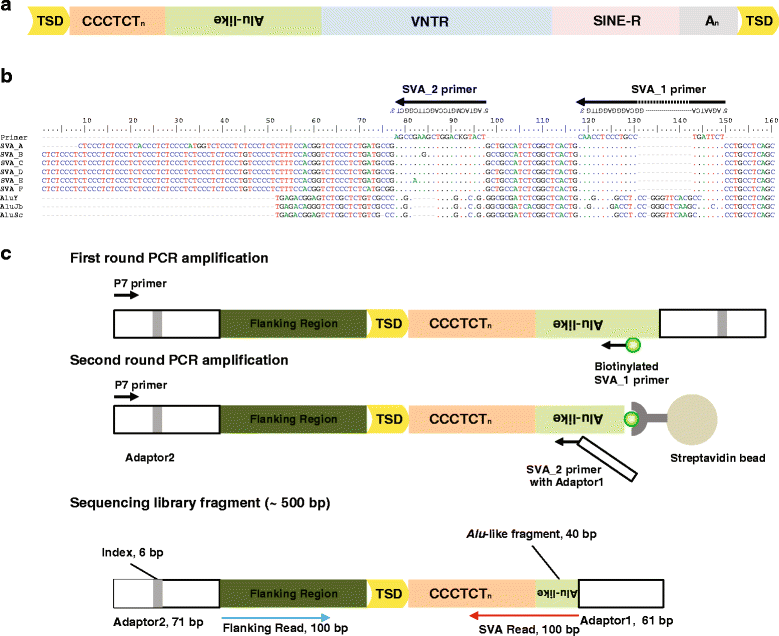
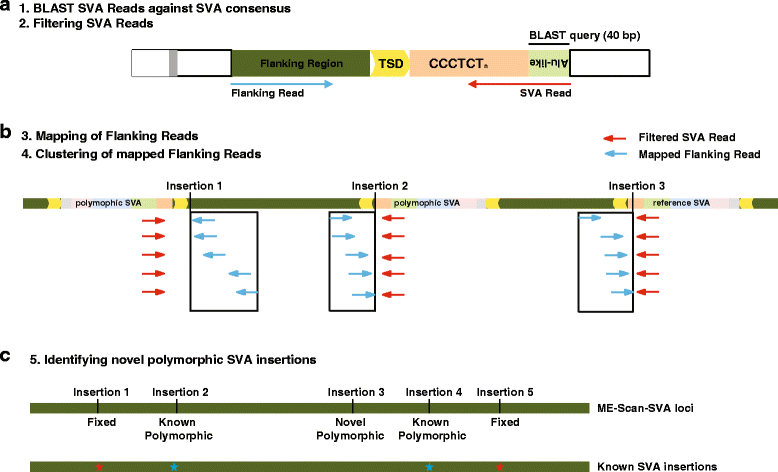
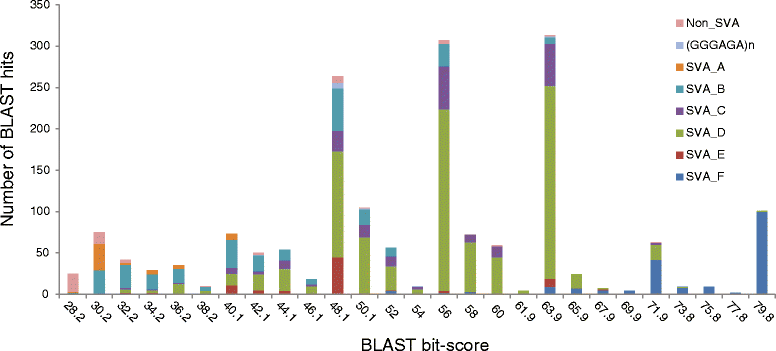
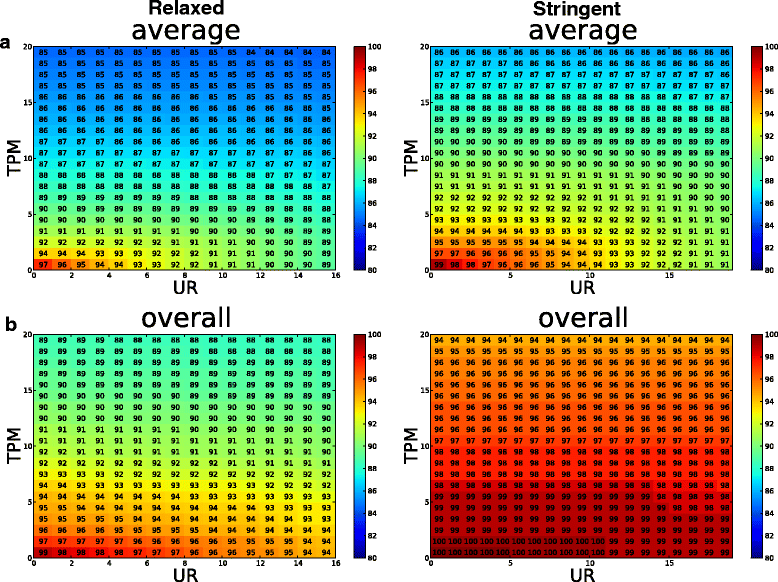
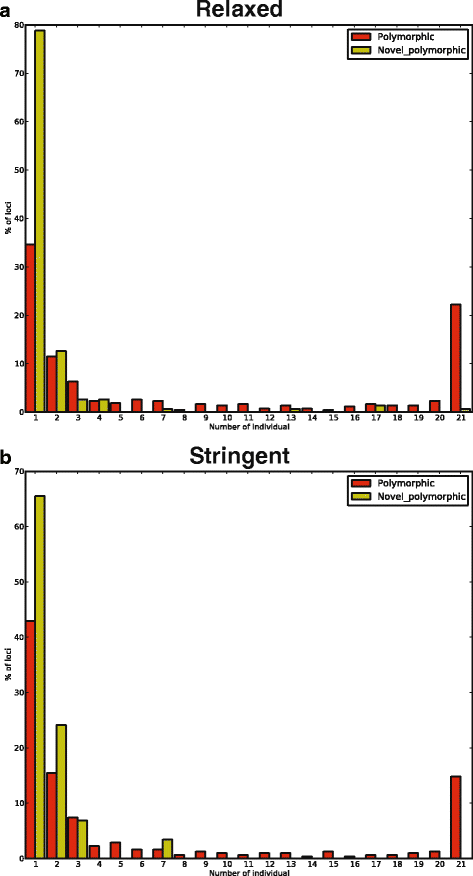
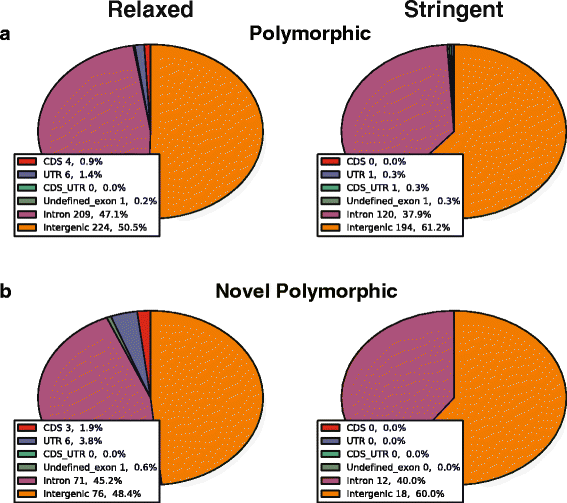
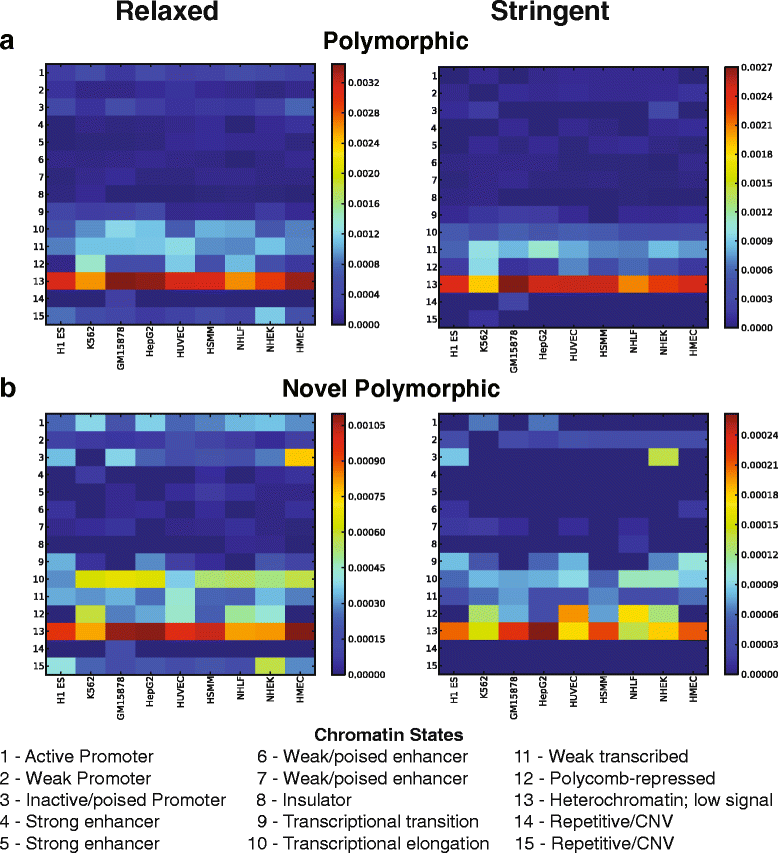
Results: To systematically identify SVA insertions at the population level and assess their genomic impact, we developed a mobile element scanning (ME-Scan) protocol we called ME-Scan-SVA. Using a nested SVA-specific PCR enrichment method, ME-Scan-SVA selectively amplify the 5' end of SVA elements and their flanking genomic regions. To demonstrate the utility of the protocol, we constructed and sequenced a ME-Scan-SVA library of 21 individuals and analyzed the data using a new analysis pipeline designed for the protocol. Overall, the method achieved high SVA-specificity and over >90 % of the sequenced reads are from SVA insertions. The method also had high sensitivity (>90 %) for fixed SVA insertions that contain the SVA-specific primer-binding sites in the reference genome. Using candidate locus selection criteria that are expected to have a 90 % sensitivity, we identified 151 and 29 novel polymorphic SVA candidates under relaxed and stringent cutoffs, respectively (average 12 and 2 per individual). For six polymorphic SVAs that we were able to validate by PCR, the average individual genotype accuracy is 92 %, demonstrating a high accuracy of the computational genotype calling pipeline.
Conclusions: The new approach allows identifying novel SVA insertions using high-throughput sequencing. It is cost-effective and can be applied in large-scale population study. It also can be applied for detecting potential active SVA elements, and somatic SVA retrotransposition events in different tissues or developmental stages.
Keywords: High-throughput sequencing; ME-Scan; Retrotransposon; SVA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated Mobile Element Scanning (ME-Scan) method for identifying multiple types of polymorphic mobile element insertions.Mob DNA. 2020 Feb 22;11:12. doi: 10.1186/s13100-020-00207-x. eCollection 2020. Mob DNA. 2020. PMID: 32110248 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile element scanning (ME-Scan) by targeted high-throughput sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2010 Jun 30;11:410. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-410. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20591181 Free PMC article.
-
The landscape of human SVA retrotransposons.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 27;51(21):11453-11465. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad821. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37823611 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of disease-associated SINE-VNTR-Alus.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 May;247(9):756-764. doi: 10.1177/15353702221082612. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35387528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SVA retrotransposons: Evolution and genetic instability.Semin Cancer Biol. 2010 Aug;20(4):234-45. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Semin Cancer Biol. 2010. PMID: 20416380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RDA coupled with deep sequencing detects somatic SVA-retrotranspositions and mosaicism in the human brain.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 1;11:1201258. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1201258. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37325565 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Mobile Element Scanning (ME-Scan) method for identifying multiple types of polymorphic mobile element insertions.Mob DNA. 2020 Feb 22;11:12. doi: 10.1186/s13100-020-00207-x. eCollection 2020. Mob DNA. 2020. PMID: 32110248 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of rare, diagnostic AluYb8/9 elements in diverse human populations.Mob DNA. 2017 Jul 27;8:9. doi: 10.1186/s13100-017-0093-0. eCollection 2017. Mob DNA. 2017. PMID: 28770012 Free PMC article.
-
Cas9 targeted enrichment of mobile elements using nanopore sequencing.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 11;12(1):3586. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23918-y. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34117247 Free PMC article.
-
Human Retrotransposons and Effective Computational Detection Methods for Next-Generation Sequencing Data.Life (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;12(10):1583. doi: 10.3390/life12101583. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

