The Anophthalmic Socket - Reconstruction Options
- PMID: 27478515
- PMCID: PMC4962761
The Anophthalmic Socket - Reconstruction Options
Abstract
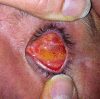
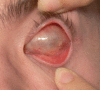
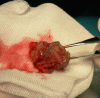
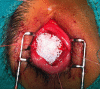
Keeping the eye is impossible, functionality is lost and aesthetic requirements are high. What do we do? Which approach is right? This is the dilemma we face whenenucleation or evisceration are unavoidable. The patient loses a sensory organ with a very important function and, at the same time, is faced with a major aesthetic defect, leading to significant anxiety. The purpose of this article is to describe the different reconstruction techniques for anophthalmic sockets. In preparing the anopthalmic socket for prosthesis fitting we have several options: dermis-fat graft with a very good biocompatibility, the Guthoff artificial implant, which provides better motility or the methyl methacrylate implant inside the muscle cone. Each option has advantages and disadvantages but the choice of technique should be adapted to the needs and expectations of the patient, taking into account both time and cost.
Keywords: anophthalmia; reconstruction.
Figures



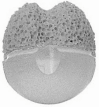
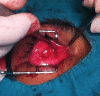
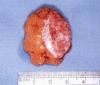



References
-
- Albert&Jakobiec’s . Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology. 3rd edition. Saunders Elsevier: 2008. volume 3, cap. 267; p. 3519.
-
- Custer PL, Trinkaus KM. Volumetric determination of enucleation implant size. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999;128:489–494. - PubMed
-
- Kaltreider SA. The ideal ocular prosthesis analysis of prosthetic volume. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;16:388–392. - PubMed
-
- Kaltreider SA, Jacobs JL, Hughes MO. Predicting the ideal implant size beforeenucleation. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;15:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Shah CT, Hughes MO, Kirzhner M. Anophthalmic syndrome : A review of management. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014 Sep-Oct;30(5):361–365. doi: 10.1097/IOP.0000000000000217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
