A Robotic Exoskeleton for Treatment of Crouch Gait in Children With Cerebral Palsy: Design and Initial Application
- PMID: 27479974
- PMCID: PMC7995637
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2595501
A Robotic Exoskeleton for Treatment of Crouch Gait in Children With Cerebral Palsy: Design and Initial Application
Abstract
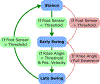
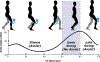
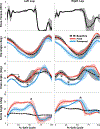
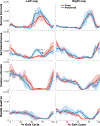
Crouch gait, a pathological pattern of walking characterized by excessive knee flexion, is one of the most common gait disorders observed in children with cerebral palsy (CP). Effective treatment of crouch during childhood is critical to maintain mobility into adulthood, yet current interventions do not adequately alleviate crouch in most individuals. Powered exoskeletons provide an untapped opportunity for intervention. The multiple contributors to crouch, including spasticity, contracture, muscle weakness, and poor motor control make design and control of such devices challenging in this population. To our knowledge, no evidence exists regarding the feasibility or efficacy of utilizing motorized assistance to alleviate knee flexion in crouch gait. Here, we present the design of and first results from a powered exoskeleton for extension assistance as a treatment for crouch gait in children with CP. Our exoskeleton, based on the architecture of a knee-ankle-foot orthosis, is lightweight (3.2 kg) and modular. On board sensors enable knee extension assistance to be provided during distinct phases of the gait cycle. We tested our device on one six-year-old male participant with spastic diplegia from CP. Our results show that the powered exoskeleton improved knee extension during stance by 18.1° while total knee range of motion improved 21.0°. Importantly, we observed no significant decrease in knee extensor muscle activity, indicating the user did not rely solely on the exoskeleton to extend the limb. These results establish the initial feasibility of robotic exoskeletons for treatment of crouch and provide impetus for continued investigation of these devices with the aim of deployment for long term gait training in this population.
Figures


References
-
- Himpens E, Van den Broeck C, Oostra A, Calders P, and Vanhaesebrouck P, “Prevalence, type, distribution, and severity of cerebral palsy in relation to gestational age: a meta-analytic review,” Dev Med Child Neurol, vol. 50, pp. 334–40, May 2008. - PubMed
-
- Odding E, Roebroeck ME, and Stam HJ, “The epidemiology of cerebral palsy: incidence, impairments and risk factors,” Disabil Rehabil, vol. 28, pp. 183–91, February 28 2006. - PubMed
-
- Yeargin-Allsopp M, Van Naarden Braun K, Doernberg NS, Benedict RE, Kirby RS, and Durkin MS, “Prevalence of cerebral palsy in 8-year-old children in three areas of the United States in 2002: a multisite collaboration,” Pediatrics, vol. 121, pp. 547–54, March 2008. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, Dan B, and Jacobsson B, “A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006,” Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl, vol. 109, pp. 8–14, February 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

