The BATTLE-2 Study: A Biomarker-Integrated Targeted Therapy Study in Previously Treated Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 27480147
- PMCID: PMC5065110
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.66.0084
The BATTLE-2 Study: A Biomarker-Integrated Targeted Therapy Study in Previously Treated Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
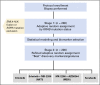
Purpose: By applying the principles of real-time biopsy, biomarker-based, adaptively randomized studies in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) established by the Biomarker-Integrated Approaches of Targeted Therapy for Lung Cancer Elimination (BATTLE) trial, we conducted BATTLE-2 (BATTLE-2 Program: A Biomarker-Integrated Targeted Therapy Study in Previously Treated Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer), an umbrella study to evaluate the effects of targeted therapies focusing on KRAS-mutated cancers.
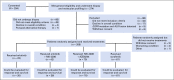
Patients and methods: Patients with advanced NSCLC (excluding sensitizing EGFR mutations and ALK gene fusions) refractory to more than one prior therapy were randomly assigned, stratified by KRAS status, to four arms: (1) erlotinib, (2) erlotinib plus MK-2206, (3) MK-2206 plus AZD6244, or (4) sorafenib. Tumor gene expression profiling-targeted next-generation sequencing was performed to evaluate predictive and prognostic biomarkers.
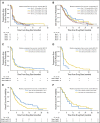
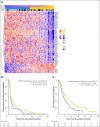
Results: Two hundred patients, 27% with KRAS-mutated (KRAS mut+) tumors, were adaptively randomly assigned to erlotinib (n = 22), erlotinib plus MK-2206 (n = 42), MK-2206 plus AZD6244 (n = 75), or sorafenib (n = 61). In all, 186 patients were evaluable, and the primary end point of an 8-week disease control rate (DCR) was 48% (arm 1, 32%; arm 2, 50%; arm 3, 53%; and arm 4, 46%). For KRAS mut+ patients, DCR was 20%, 25%, 62%, and 44% whereas for KRAS wild-type patients, DCR was 36%, 57%, 49%, and 47% for arms 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Median progression-free survival was 2.0 months, not different by KRAS status, 1.8 months for arm 1, and 2.5 months for arms 2 versus arms 3 and 4 in KRAS mut+ patients (P = .04). Median overall survival was 6.5 months, 9.0 and 5.1 months for arms 1 and 2 versus arms 3 and 4 in KRAS wild-type patients (P = .03). Median overall survival was 7.5 months in mesenchymal versus 5 months in epithelial tumors (P = .02).
Conclusion: Despite improved progression-free survival on therapy that did not contain erlotinib for KRAS mut+ patients and improved prognosis for mesenchymal tumors, better biomarker-driven treatment strategies are still needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures
Comment in
-
Precision medicine in lung cancer: the battle continues.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Nov;8(11):2991-2993. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.11.46. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 28066565 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lessons learned from BATTLE-2 in the war on cancer: the use of Bayesian method in clinical trial design.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Dec;4(23):466. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.11.48. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 28090522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Going into BATTLE: umbrella and basket clinical trials to accelerate the study of biomarker-based therapies.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Dec;4(24):529. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.12.57. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 28149890 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Le Chevalier T, Scagliotti G, Natale R, et al. Efficacy of gemcitabine plus platinum chemotherapy compared with other platinum containing regimens in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of survival outcomes. Lung Cancer. 2005;47:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Toyooka S, Mitsudomi T, Soh J, et al. Molecular oncology of lung cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;59:527–537. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

