Original Research: miR-194 inhibits proliferation and invasion and promotes apoptosis by targeting KDM5B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 27480251
- PMCID: PMC5206979
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370216662712
Original Research: miR-194 inhibits proliferation and invasion and promotes apoptosis by targeting KDM5B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
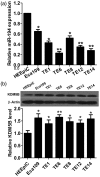
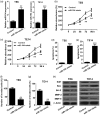
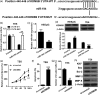
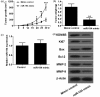
Increasing evidence suggests that miR-194 is down-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumor tissue. However, the role and underlying mechanism of miR-194 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma have not been well defined. We used DIANA, TargetScan and miRanda to perform target prediction analysis and found KDM5B is a potential target of miR-194. Based on these findings, we speculated that miR-194 might play a role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development and progression by regulation the expression of KDM5B. We detected the expression of miR-194 and KDM5B by quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot assays, respectively, and found down-regulation of miR-194 and up-regulation of KDM5B existed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. By detecting proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of TE6 and TE14 cells transfected with miR-194 mimics or mimic control, miR-194 was found to inhibit proliferation and invasion and promote apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. miR-194 was further verified to regulate proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by directly targeting KDM5B. Furthermore, animal studies were performed and showed that overexpression of miR-194 inhibited the growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumors in vivo. These results confirmed our speculation that miR-194 targets KDM5B to inhibit esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development and progression. These findings offer new clues for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development and progression and novel potential therapeutic targets for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; apoptosis; histone demethylase lysine demethylase 5b; miR-194; proliferation.
© 2016 by the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-194 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by targeting KDM5B.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Nov;20(21):4487-4493. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27874950
-
Aberrant KDM5B expression promotes aggressive breast cancer through MALAT1 overexpression and downregulation of hsa-miR-448.BMC Cancer. 2016 Feb 25;16:160. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2108-5. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26917489 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-214 promotes cell meastasis and inhibites apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Sep;105:350-361. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.149. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29864623
-
MicroRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Cancer Biomark. 2017;19(1):1-9. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160240. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28269750 Review.
-
Molecular interplay of pro-inflammatory transcription factors and non-coding RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2017 Jun;39(6):1010428317705760. doi: 10.1177/1010428317705760. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28618941 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-139-3p Inhibits Malignant Behaviors of Laryngeal Cancer Cells via the KDM5B/SOX2 Axis and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Sep 28;12:9197-9209. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S268871. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33061611 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Chemoresistance in Adenocarcinomas of the Esophagogastric Junction.J Oncol. 2019 Jul 29;2019:4903152. doi: 10.1155/2019/4903152. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31467538 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Significance of Histone Lysine Demethylases as Prognostic Markers and Therapeutic Targets in Head and Neck Cancers.Cells. 2022 Mar 17;11(6):1023. doi: 10.3390/cells11061023. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35326475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming radio-resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via hypermethylation of PIK3C3 promoter region mediated by KDM5B loss.J Radiat Res. 2022 May 18;63(3):331-341. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrac004. J Radiat Res. 2022. PMID: 35333349 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA let-7i Inhibits Histone Lysine Demethylase KDM5B to Halt Esophageal Cancer Progression.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 16;22:846-861. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.012. eCollection 2020 Dec 4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 33230480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2241–52. - PubMed
-
- Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Karashima R, Sato N, Imamura Y, Nagai Y, Yoshida N, Toyama E, Hayashi N, Watanabe M. MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 1915–22. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Leung AC, Ko JM, Lo PH, Tang JC, Srivastava G, Oshimura M, Stanbridge EJ, Daigo Y, Nakamura Y. Tumor suppressive role of a 2.4 Mb 9q33–q34 critical region and DEC1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2005; 24: 697–705. - PubMed
-
- Hobert O. Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science 2008; 319: 1785–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

