Clinical and Experimental Sepsis Impairs CD8 T-Cell-Mediated Immunity
- PMID: 27480902
- PMCID: PMC5314458
- DOI: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2016017098
Clinical and Experimental Sepsis Impairs CD8 T-Cell-Mediated Immunity
Abstract
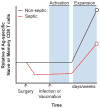
Septic patients experience chronic immunosuppression resulting in enhanced susceptibility to infections normally controlled by T cells. Clinical research on septic patients has shown increased apoptosis and reduced total numbers of CD4 and CD8 T cells, suggesting contributing mechanism driving immunosuppression. Experimental models of sepsis, including cecal ligation and puncture, reverse translated this clinical observation to facilitate hypothesis-driven research and allow the use of an array of experimental tools to probe the impact of sepsis on T-cell immunity. In addition to numerical loss, sepsis functionally impairs the antigen-driven proliferative capacity and effector functions of CD4 and CD8 T cells. Sepsis-induced impairments in both the quantity and quality of T cells results in reduced protective capacity and increased susceptibility of mice to new or previously encountered infections. Therefore, the combined efforts of clinical and experimental sepsis research have begun to elucidate the impact of sepsis on T-cell-mediated immunity and potential T-cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic mechanisms driving chronic immunosuppression. Future work will explore the impact of sepsis on the recently appreciated tissue-resident memory (TRM) T cells, which provide robust protection against localized infections, and dendritic cells, which are needed to activate T cells and promote effective T-cell responses.
Figures

References
-
- Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC, Reinhart K International Forum of Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis: current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:259–72. - PubMed
-
- Lagu T, Rothberg MB, Shieh MS, Pekow PS, Steingrub JS, Lindenauer PK. Hospitalizations, costs, and outcomes of severe sepsis in the United States 2003 to 2007. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:754–61. - PubMed
-
- Kumar G, Kumar N, Taneja A, Kaleekal T, Tarima S, McGinley E, Jimenez E, Mohan A, Khan RA, Whittle J, Jacobs E, Nanchal R Milwaukee Initiative in Critical Care Outcomes Research Group of Investigators. Nationwide trends of severe sepsis in the 21st century (2000–2007) Chest. 2011;140:1223–31. - PubMed
-
- Leligdowicz A, Dodek PM, Norena M, Wong H, Kumar A, Kumar A Co-operative Antimicrobial Therapy of Septic Shock Database Research G. Association between source of infection and hospital mortality in patients who have septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:1204–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

