Signaling Receptors for TGF-β Family Members
- PMID: 27481709
- PMCID: PMC4968163
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022053
Signaling Receptors for TGF-β Family Members
Abstract
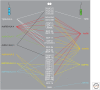
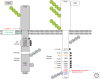
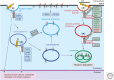
Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family members signal via heterotetrameric complexes of type I and type II dual specificity kinase receptors. The activation and stability of the receptors are controlled by posttranslational modifications, such as phosphorylation, ubiquitylation, sumoylation, and neddylation, as well as by interaction with other proteins at the cell surface and in the cytoplasm. Activation of TGF-β receptors induces signaling via formation of Smad complexes that are translocated to the nucleus where they act as transcription factors, as well as via non-Smad pathways, including the Erk1/2, JNK and p38 MAP kinase pathways, and the Src tyrosine kinase, phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase, and Rho GTPases.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abdalla SA, Cymerman U, Rushlow D, Chen N, Stoeber GP, Lemire EG, Letarte M. 2005. Novel mutations and polymorphisms in genes causing hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Hum Mutat 25: 320–321. - PubMed
-
- Abdollah S, Macías-Silva M, Tsukazaki T, Hayashi H, Attisano L, Wrana JL. 1997. TβRI phosphorylation of Smad2 on Ser465 and Ser467 is required for Smad2–Smad4 complex formation and signaling. J Biol Chem 272: 27678–27685. - PubMed
-
- Arthur HM, Ure J, Smith AJ, Renforth G, Wilson DI, Torsney E, Charlton R, Parums DV, Jowett T, Marchuk DA, et al. 2000. Endoglin, an ancillary TGFβ receptor, is required for extraembryonic angiogenesis and plays a key role in heart development. Dev Biol 217: 42–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
