Deciphering the Molecular and Functional Basis of RHOGAP Family Proteins: A SYSTEMATIC APPROACH TOWARD SELECTIVE INACTIVATION OF RHO FAMILY PROTEINS
- PMID: 27481945
- PMCID: PMC5034035
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.736967
Deciphering the Molecular and Functional Basis of RHOGAP Family Proteins: A SYSTEMATIC APPROACH TOWARD SELECTIVE INACTIVATION OF RHO FAMILY PROTEINS
Abstract
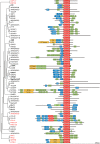
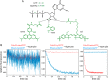
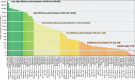
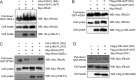
RHO GTPase-activating proteins (RHOGAPs) are one of the major classes of regulators of the RHO-related protein family that are crucial in many cellular processes, motility, contractility, growth, differentiation, and development. Using database searches, we extracted 66 distinct human RHOGAPs, from which 57 have a common catalytic domain capable of terminating RHO protein signaling by stimulating the slow intrinsic GTP hydrolysis (GTPase) reaction. The specificity of the majority of the members of RHOGAP family is largely uncharacterized. Here, we comprehensively investigated the sequence-structure-function relationship between RHOGAPs and RHO proteins by combining our in vitro data with in silico data. The activity of 14 representatives of the RHOGAP family toward 12 RHO family proteins was determined in real time. We identified and structurally verified hot spots in the interface between RHOGAPs and RHO proteins as critical determinants for binding and catalysis. We have found that the RHOGAP domain itself is nonselective and in some cases rather inefficient under cell-free conditions. Thus, we propose that other domains of RHOGAPs confer substrate specificity and fine-tune their catalytic efficiency in cells.
Keywords: GTPase; GTPase-activating protein (GAP); RAC (RAC GTPase); Ras homolog gene family, member A (RHOA); arginine finger; crystal structure; deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC1); protein-protein interaction; signal transduction; substrate specificity.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Jaiswal M., Dubey B. N., Koessmeier K. T., Gremer L., and Ahmadian M. R. (2012) in Rho GTPases Methods and Protocols (Rivero F., ed) pp. 37–58, Springer, Germany - PubMed
-
- Zhang B., and Zheng Y. (1998) Regulation of RhoA GTP hydrolysis by the GTPase-activating proteins p190, p50RhoGAP, Bcr, and 3BP-1. Biochemistry 37, 5249–5257 - PubMed
-
- Fidyk N. J., and Cerione R. A. (2002) Understanding the catalytic mechanism of GTPase-activating proteins: demonstration of the importance of switch domain stabilization in the stimulation of GTP hydrolysis. Biochemistry 41, 15644–15653 - PubMed
-
- Haeusler L. C., Blumenstein L., Stege P., Dvorsky R., and Ahmadian M. R. (2003) Comparative functional analysis of the RAC GTPases. FEBS Lett. 555, 556–560 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

