Early, Isolated Duodenal Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Presenting without Symptoms or Grossly Apparent Endoscopic Lesions and Diagnosed by Random Duodenal Biopsies
- PMID: 27482191
- PMCID: PMC4945810
- DOI: 10.1159/000447293
Early, Isolated Duodenal Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Presenting without Symptoms or Grossly Apparent Endoscopic Lesions and Diagnosed by Random Duodenal Biopsies
Abstract
Clinical data regarding mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALToma) solely involving the duodenum are sparse because of the relative rarity of the disease. A comprehensive literature review revealed only 17 cases reported until 2004, and only a moderate number of cases have been reported since. MALToma can be asymptomatic in its very early stages but frequently produces localized or nonspecific symptoms, including early satiety, abdominal pain, vomiting, and involuntary weight loss in later stages. While gastric MALToma is strongly associated with gastric Helicobactor pylori infection, duodenal MALToma is often unassociated with H. pylori infection. A 74-year-old female presented with only dysphagia (without symptoms referable to a duodenal lesion), without systemic 'B' symptoms, and with no evident duodenal lesions at esophagogastroduodenoscopy; however, she was diagnosed with duodenal MALToma by pathologic examination of random duodenal biopsies performed to exclude celiac disease. An important clinical feature of this case is that duodenal MALToma was diagnosed by pathologic analysis of duodenal biopsies despite (1) no endoscopically apparent duodenal lesions; (2) duodenal involvement without gastric involvement; (3) lack of symptoms attributable to duodenal MALToma, and (4) absence of evident H. pylori infection. This work shows that early duodenal MALToma can be difficult to diagnose because of absent symptoms, absence of gastric involvement, absence of endoscopic abnormalities, and absence of H. pylori infection; it may require random duodenal biopsies for diagnosis.
Keywords: Duodenum; Esophagogastroduodenoscopy; Helicobacter pylori; Lymphoma; Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma.
Figures
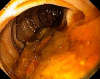
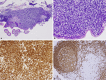
References
-
- A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma The Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. Blood. 1997;89:3909–3918. - PubMed
-
- Xu X, Wang Z, Yu Y, Wang Y, Zhang L, Sun B, Da W, Zhang Y. Evaluation of the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of gastrointestinal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:1678–1684. - PubMed
-
- Zucca E, Bertoni F, Roggero E, Bosshard G, Cazzaniga G, Pedrinis E, Biondi A, Cavalli F. Molecular analysis of the progression from Helicobacter pylori-associated chronic gastritis to mucosa-associated lymphoid-tissue lymphoma of the stomach. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:804–810. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

