Blonanserin Augmentation of Atypical Antipsychotics in Patients with Schizophrenia-Who Benefits from Blonanserin Augmentation?: An Open-Label, Prospective, Multicenter Study
- PMID: 27482249
- PMCID: PMC4965658
- DOI: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.4.458
Blonanserin Augmentation of Atypical Antipsychotics in Patients with Schizophrenia-Who Benefits from Blonanserin Augmentation?: An Open-Label, Prospective, Multicenter Study
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the efficacy and tolerability of atypical antipsychotics (AAPs) with augmentation by blonanserin in schizophrenic patients.
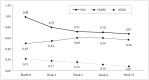
Methods: aA total of 100 patients with schizophrenia who were partially or completely unresponsive to treatment with an AAP were recruited in this 12-week, open-label, non-comparative, multicenter study. Blonanserin was added to their existing AAP regimen, which was maintained during the study period. Efficacy was primarily evaluated using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) at baseline and at weeks 2, 4, 8, and 12. Predictors for PANSS response (≥20% reduction) were investigated.
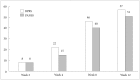
Results: The PANSS total score was significantly decreased at 12 weeks of blonanserin augmentation (-21.0±18.1, F=105.849, p<0.001). Moreover, 51.0% of participants experienced a response at week 12. Premature discontinuation of blonanserin occurred in 17 patients (17.0%); 4 of these patients dropped out due to adverse events. The patients who benefited the most from blonanserin were those with severe symptoms despite a treatment with a higher dose of AAP.
Conclusion: Blonanserin augmentation could be an effective strategy for patients with schizophrenia who were partially or completely unresponsive to treatment with an AAP.
Keywords: Antipsychotics; Augmentation; Blonanserin; Schizophrenia; Treatment response.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Switching Antipsychotics to Blonanserin in Patients with Schizophrenia: An Open-label, Prospective, Multicenter Study.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2019 Aug 31;17(3):423-431. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2019.17.3.423. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31352709 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term oral blonanserin treatment for schizophrenia: a review of Japanese long-term studies.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 7;20(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12991-021-00361-3. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34493318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Blonanserin Oral Tablet in Adolescents with Schizophrenia: A 52-Week, Multicenter, Open-Label Extension Study.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2022 Feb;32(1):24-35. doi: 10.1089/cap.2021.0058. Epub 2021 Oct 5. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34612724 Free PMC article.
-
Switching antipsychotics to aripiprazole or blonanserin and plasma monoamine metabolites levels in patients with schizophrenia.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2014 Mar;29(2):199-202. doi: 10.1002/hup.2386. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24590545 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy, Tolerability, and Safety of Blonanserin in Schizophrenia: An Updated and Extended Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2019 Feb;52(2):52-62. doi: 10.1055/a-0574-0088. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2019. PMID: 29514360
Cited by
-
Who can benefit more from its twelve-week treatment: A prospective cohort study of blonanserin for patients with schizophrenia.World J Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 19;14(11):1735-1745. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i11.1735. eCollection 2024 Nov 19. World J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39564169 Free PMC article.
-
Switching Antipsychotics to Blonanserin in Patients with Schizophrenia: An Open-label, Prospective, Multicenter Study.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2019 Aug 31;17(3):423-431. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2019.17.3.423. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31352709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Hert M, van Winkel R, Wampers M, Kane J, van Os J, Peuskens J. Remission criteria for schizophrenia: evaluation in a large naturalistic cohort. Schizophr Res. 2007;92:68–73. - PubMed
-
- Hegarty JD, Baldessarini RJ, Tohen M, Waternaux C, Oepen G. One hundred years of schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of the outcome literature. Am J Psychiatry. 1994;151:1409–1416. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, et al. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1209–1223. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

