Telomeres in aging and disease: lessons from zebrafish
- PMID: 27482813
- PMCID: PMC4958310
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.025130
Telomeres in aging and disease: lessons from zebrafish
Abstract
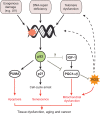
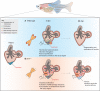
Age is the highest risk factor for some of the most prevalent human diseases, including cancer. Telomere shortening is thought to play a central role in the aging process in humans. The link between telomeres and aging is highlighted by the fact that genetic diseases causing telomerase deficiency are associated with premature aging and increased risk of cancer. For the last two decades, this link has been mostly investigated using mice that have long telomeres. However, zebrafish has recently emerged as a powerful and complementary model system to study telomere biology. Zebrafish possess human-like short telomeres that progressively decline with age, reaching lengths in old age that are observed when telomerase is mutated. The extensive characterization of its well-conserved molecular and cellular physiology makes this vertebrate an excellent model to unravel the underlying relationship between telomere shortening, tissue regeneration, aging and disease. In this Review, we explore the advantages of using zebrafish in telomere research and discuss the primary discoveries made in this model that have contributed to expanding our knowledge of how telomere attrition contributes to cellular senescence, organ dysfunction and disease.
Keywords: Aging; Cancer; Disease; Telomerase; Telomeres; Zebrafish.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alcaraz-Pérez F., García-Castillo J., García-Moreno D., López-Muñoz A., Anchelin M., Angosto D., Zon L. I., Mulero V. and Cayuela M. L. (2014). A non-canonical function of telomerase RNA in the regulation of developmental myelopoiesis in zebrafish. Nat. Commun. 5, 3228 10.1038/ncomms4228 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

