Dasatinib induces lung vascular toxicity and predisposes to pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 27482885
- PMCID: PMC5004960
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI86249
Dasatinib induces lung vascular toxicity and predisposes to pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
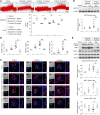
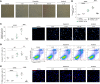
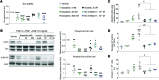
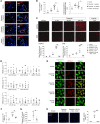
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening disease that can be induced by dasatinib, a dual Src and BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). Today, key questions remain regarding the mechanisms involved in the long-term development of dasatinib-induced PAH. Here, we demonstrated that chronic dasatinib therapy causes pulmonary endothelial damage in humans and rodents. We found that dasatinib treatment attenuated hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction responses and increased susceptibility to experimental pulmonary hypertension (PH) in rats, but these effects were absent in rats treated with imatinib, another BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Furthermore, dasatinib treatment induced pulmonary endothelial cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner, while imatinib did not. Dasatinib treatment mediated endothelial cell dysfunction via increased production of ROS that was independent of Src family kinases. Consistent with these findings, we observed elevations in markers of endothelial dysfunction and vascular damage in the serum of CML patients who were treated with dasatinib, compared with CML patients treated with imatinib. Taken together, our findings indicate that dasatinib causes pulmonary vascular damage, induction of ER stress, and mitochondrial ROS production, which leads to increased susceptibility to PH development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of dasatinib and imatinib on physiological parameters of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;79(4):711-723. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3264-2. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28283735
-
Real-time analysis of imatinib- and dasatinib-induced effects on chronic myelogenous leukemia cell interaction with fibronectin.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 8;9(9):e107367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107367. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25198091 Free PMC article.
-
Cotreatment with vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) enhances activity of dasatinib (BMS-354825) against imatinib mesylate-sensitive or imatinib mesylate-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 1;12(19):5869-78. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0980. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17020995
-
Pulmonary complications of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Eur Respir J. 2020 Oct 29;56(4):2000279. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00279-2020. Print 2020 Oct. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32527740 Review.
-
Clinical features of pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients receiving dasatinib.Am J Hematol. 2015 Nov;90(11):1060-4. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24174. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Am J Hematol. 2015. PMID: 26284693 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Therapy-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Ventricular Dysfunction: Etiologies and Prognostic Implications.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Mar 5;25(3):87. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2503087. eCollection 2024 Mar. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39076943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin Attenuates Dasatinib-Aggravated Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension via Inhibiting Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Mar 24;9:790921. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.790921. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35402542 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Molecular Mechanisms in Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Ventricle Dysfunction.Front Physiol. 2018 Dec 10;9:1777. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01777. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30618793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pharmacology and Rationale for Seralutinib in the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 10;24(16):12653. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612653. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors relax pulmonary arteries in human and murine precision-cut lung slices.Respir Res. 2019 Jun 6;20(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1074-2. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31170998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galiè N, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Respir J. 2015;46(4):903–975. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01032-2015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

