Clinical Evaluation of the BD FACSPresto™ Near-Patient CD4 Counter in Kenya
- PMID: 27483008
- PMCID: PMC4970792
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157939
Clinical Evaluation of the BD FACSPresto™ Near-Patient CD4 Counter in Kenya
Abstract
Background: The BD FACSPresto™ Near-Patient CD4 Counter was developed to expand HIV/AIDS management in resource-limited settings. It measures absolute CD4 counts (AbsCD4), percent CD4 (%CD4), and hemoglobin (Hb) from a single drop of capillary or venous blood in approximately 23 minutes, with throughput of 10 samples per hour. We assessed the performance of the BD FACSPresto system, evaluating accuracy, stability, linearity, precision, and reference intervals using capillary and venous blood at KEMRI/CDC HIV-research laboratory, Kisumu, Kenya, and precision and linearity at BD Biosciences, California, USA.
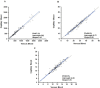
Methods: For accuracy, venous samples were tested using the BD FACSCalibur™ instrument with BD Tritest™ CD3/CD4/CD45 reagent, BD Trucount™ tubes, and BD Multiset™ software for AbsCD4 and %CD4, and the Sysmex™ KX-21N for Hb. Stability studies evaluated duration of staining (18-120-minute incubation), and effects of venous blood storage <6-24 hours post-draw. A normal cohort was tested for reference intervals. Precision covered multiple days, operators, and instruments. Linearity required mixing two pools of samples, to obtain evenly spaced concentrations for AbsCD4, total lymphocytes, and Hb.
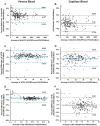
Results: AbsCD4 and %CD4 venous/capillary (N = 189/ N = 162) accuracy results gave Deming regression slopes within 0.97-1.03 and R2 ≥0.96. For Hb, Deming regression results were R2 ≥0.94 and slope ≥0.94 for both venous and capillary samples. Stability varied within 10% 2 hours after staining and for venous blood stored less than 24 hours. Reference intervals results showed that gender-but not age-differences were statistically significant (p<0.05). Precision results had <3.5% coefficient of variation for AbsCD4, %CD4, and Hb, except for low AbsCD4 samples (<6.8%). Linearity was 42-4,897 cells/μL for AbsCD4, 182-11,704 cells/μL for total lymphocytes, and 2-24 g/dL for Hb.
Conclusions: The BD FACSPresto system provides accurate, precise clinical results for capillary or venous blood samples and is suitable for near-patient CD4 testing.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02396355.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lawn S, Myer L, Orrell C, Bekker L, Wood R. Early mortality among adults accessing a community-based antiretroviral service in South Africa: implications for programme design. AIDS. 2005;19(18):2141–8. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1997. Revised Guidelines for Performning CD4+ T-Cell Determinations in Persons Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). MMWR 1997; 46 (No. RR-2): 2–22. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1998. Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Pediatric HIV Infection. MMWR 1998; 47(No: RR-4:3–26. - PubMed
-
- World Hhealth Organization. Antiretroviral therapy HIV infection in adults and adolescents. Recommendations for a public health approach: 2010 revision. Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

