Reproducibility and uptake time dependency of volume-based parameters on FDG-PET for lung cancer
- PMID: 27484805
- PMCID: PMC4969656
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2624-3
Reproducibility and uptake time dependency of volume-based parameters on FDG-PET for lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Volume-based parameters, such as metabolic tumor volume (MTV) and total lesion glycolysis (TLG), on F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) are useful for predicting treatment response in nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We aimed to examine intra- and inter-operator reproducibility to measure the MTV and TLG, and to estimate their dependency on the uptake time.
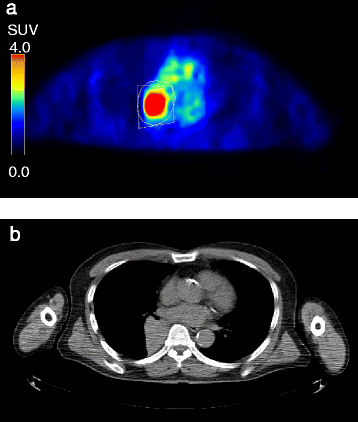
Methods: Fifty NSCLC patients underwent preoperative FDG-PET. After an injection of FDG, the whole body was scanned twice: at the early phase (61.4 ± 2.8 min) and delayed phase (117.7 ± 1.6 min). Two operators independently defined the tumor boundary using three different delineation methods: (1) the absolute SUV threshold method (MTVp and TLGp; p = 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5), (2) the fixed% SUVmax threshold method (MTVq% and TLGq%; q = 35, 40, 45), and (3) the adaptive region-growing method (MTVARG and TLGARG). Parameters were compared between operators and between phases.
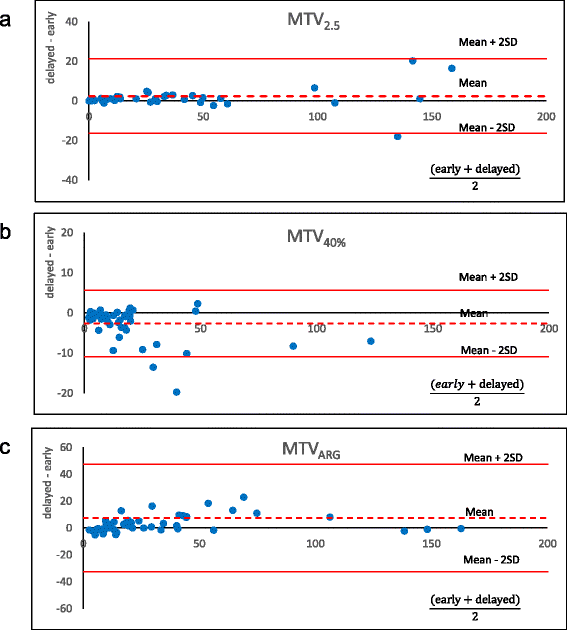
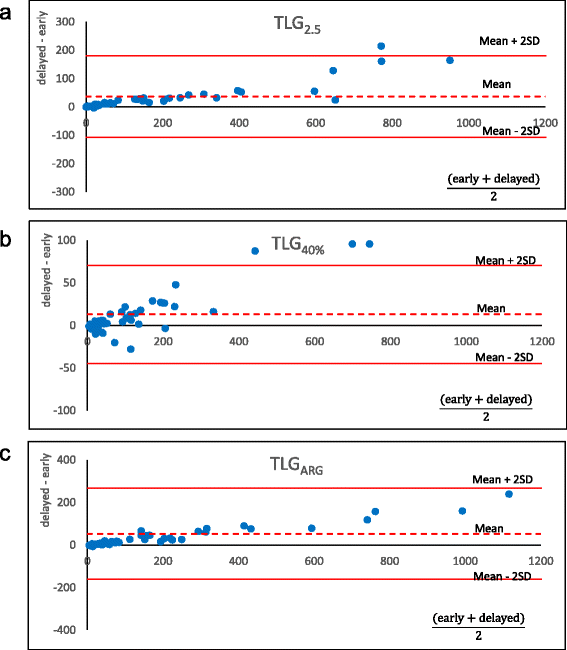
Results: Both the intra- and inter-operator reproducibility were high for all parameters using any method (intra-class correlation > 0.99 each). MTV3.0 and MTV3.5 resulted in a significant increase from the early to delayed phase (P < 0.05 for both), whereas MTV2.0 and MTV2.5 neither increased nor decreased (P = n.s.). All of the MTVq% values significantly decreased over time (P < 0.01), whereas MTVARG and TLG with any delineation method increased significantly (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: High reproducibility of MTV and TLG was obtained by all of the methods used. MTV2.0 and MTV2.5 were the least sensitive to uptake time, and may be good alternatives when we compare images acquired with different uptake times, although applying constant uptake time is important for volume measurement.
Keywords: FDG-PET; Lung cancer; Metabolic tumor volume; Reproducibility; Total lesion glycolysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of metabolic tumor burden from (18)F-FDG PET in surgical patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Acad Radiol. 2013 Jan;20(1):32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Acad Radiol. 2013. PMID: 22999369
-
Prognostic value of whole-body total lesion glycolysis at pretreatment FDG PET/CT in non-small cell lung cancer.Radiology. 2012 Aug;264(2):559-66. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12111148. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Radiology. 2012. PMID: 22692034
-
Consistency of metabolic tumor volume of non-small-cell lung cancer primary tumor measured using 18F-FDG PET/CT at two different tracer uptake times.Nucl Med Commun. 2016 Jan;37(1):50-6. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000396. Nucl Med Commun. 2016. PMID: 26426969 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Surgical Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 4;11(1):e0146195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146195. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26727114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of volumetric parameters of (18)F-FDG PET in non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Feb;42(2):241-51. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2903-7. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25193652
Cited by
-
The reproducibility of MTV and TLG of soft tissue tumors calculated by FDG-PET: Comparison between the lower limit by the fixed value SUV 2.5 and that value by 30% of SUVmax.Jpn J Radiol. 2023 May;41(5):531-540. doi: 10.1007/s11604-022-01378-8. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Jpn J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36637680 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic bulk volume predicts survival in a homogeneous cohort of stage II/III diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients undergoing R-CHOP treatment.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 13;13:1186311. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1186311. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37384292 Free PMC article.
-
A Preliminary Study to Use SUVmax of FDG PET-CT as an Identifier of Lesion for Artificial Intelligence.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 28;8:647562. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.647562. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33996855 Free PMC article.
-
FDG-PET/CT in the Monitoring of Lymphoma Immunotherapy Response: Current Status and Future Prospects.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;15(4):1063. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041063. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative FDG PET Assessment for Oncology Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 19;13(4):869. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040869. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33669531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jhanwar YS, Straus DJ. The role of PET in lymphoma. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(8):1326–34. - PubMed
-
- Israel O, Kuten A. Early detection of cancer recurrence: 18 F-FDG PET/CT can make a difference in diagnosis and patient care. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(Suppl 1):28S–35. - PubMed
-
- Inoue T, Kim EE, Komaki R, Wong FC, Bassa P, Wong WH, et al. Detecting recurrent or residual lung cancer with FDG-PET. J Nucl Med. 1995;36(5):788–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

