Atomic resolution mechanistic studies of ribocil: A highly selective unnatural ligand mimic of the E. coli FMN riboswitch
- PMID: 27485612
- PMCID: PMC5056776
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1216304
Atomic resolution mechanistic studies of ribocil: A highly selective unnatural ligand mimic of the E. coli FMN riboswitch
Abstract
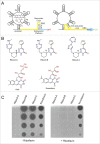
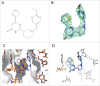
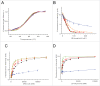
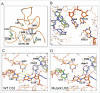
Bacterial riboswitches are non-coding RNA structural elements that direct gene expression in numerous metabolic pathways. The key regulatory roles of riboswitches, and the urgent need for new classes of antibiotics to treat multi-drug resistant bacteria, has led to efforts to develop small-molecules that mimic natural riboswitch ligands to inhibit metabolic pathways and bacterial growth. Recently, we reported the results of a phenotypic screen targeting the riboflavin biosynthesis pathway in the Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli that led to the identification of ribocil, a small molecule inhibitor of the flavin mononucleotide (FMN) riboswitch controlling expression of this biosynthetic pathway. Although ribocil is structurally distinct from FMN, ribocil functions as a potent and highly selective synthetic mimic of the natural ligand to repress riboswitch-mediated ribB gene expression and inhibit bacterial growth both in vitro and in vivo. Herein, we expand our analysis of ribocil; including mode of binding in the FMN binding pocket of the riboswitch, mechanisms of resistance and structure-activity relationship guided efforts to generate more potent analogs.
Keywords: Antibiotics; FMN riboswitch; RNA regulatory element; riboflavin.
Figures

References
-
- Serganov A, Nudler A. A decade of riboswitches. Cell 2013; 152:17-24; PMID:23332744; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mellin JR, Cossart P. Unexpected versatility in bacterial riboswitches. Trends Genet 2015; 31:150-56; PMID:25708284; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2015.01.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Winkler WC, Breaker RR. Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches. Annu Rev Microbiol 2005; 59:487-517; PMID:16153177; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.59.030804.121336 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breaker RR. 2011. Prospects for riboswitch discovery and analysis. Mol Cell 2011; 43:867-79; PMID:21925376; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lünse CE, Schüller A, Mayer G. The promise of riboswitches as potential antibacterial drug targets. Int J Med Microbiol 2014; 304:79-92; PMID:24140145; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.09.002 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
