Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Consensus Report: Current Status, Challenges, and Priorities
- PMID: 27486237
- PMCID: PMC5314694
- DOI: 10.2337/dc16-1066
Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Consensus Report: Current Status, Challenges, and Priorities
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes is a significant and increasing burden in adolescents and young adults. Clear strategies for research, prevention, and treatment of the disease in these vulnerable patients are needed. Evidence suggests that type 2 diabetes in children is different not only from type 1 but also from type 2 diabetes in adults. Understanding the unique pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes in youth, as well as the risk of complications and the psychosocial impact, will enable industry, academia, funding agencies, advocacy groups, and regulators to collectively evaluate both current and future research, treatment, and prevention approaches. This Consensus Report characterizes type 2 diabetes in children, evaluates the fundamental differences between childhood and adult disease, describes the current therapeutic options, and discusses challenges to and approaches for developing new treatments.
© 2016 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

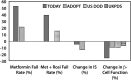

References
-
- Zeitler P, Chou HS, Copeland KC, Geffner M. Clinical trials in youth-onset type 2 diabetes: needs, barriers, and options. Curr Diab Rep 2015;15:28. - PubMed
-
- Berends LM, Ozanne SE. Early determinants of type-2 diabetes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;26:569–580 - PubMed
-
- Lawrence JM, Imperatore G, Pettitt DJ, et al. . Incidence of diabetes in United States youth by diabetes type, race/ethnicity, and age, 2008–2009 (Abstract). Diabetes 2014;63(Suppl. 1):A407
-
- Fazeli Farsani S, van der Aa MP, van der Vorst MMJ, Knibbe CA, de Boer A. Global trends in the incidence and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents: a systematic review and evaluation of methodological approaches. Diabetologia 2013;56:1471–1488 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

