The Paraoxonase 1 Arylesterase Activity, Total Oxidative Stress, Nitric Oxide and Vitamin C Levels in Maternal Serum, and Their Relation to Birth Weight of Newborn
- PMID: 27486277
- PMCID: PMC4958076
- DOI: 10.1007/s13224-015-0704-y
The Paraoxonase 1 Arylesterase Activity, Total Oxidative Stress, Nitric Oxide and Vitamin C Levels in Maternal Serum, and Their Relation to Birth Weight of Newborn
Abstract
Aim: Aim of this study is to find out clinical relevance of estimating PON1 arylesterase activity, total oxidative stress (TOS), nitric oxide (NO), and vitamin C levels in maternal serum for prediction of birth weight of newborn.
Methods: We have investigated the PON1 arylesterase activity, TOS, NO, vitamin C, total protein, and albumin levels in 56 postnatal clinic patients having newborn weighing <2500 gm (low birth weight) and compared with 56 postnatal clinic patients having newborn weighing >2500 gm. Samples were collected immediately after delivery.
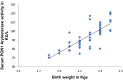
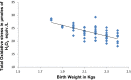
Results: PON1 arylesterase activity levels show significant decrease in cases as compared to controls (93.27 ± 13.76 kU/l vs. 112.77 ± 9.42 kU/l). Nitric oxide (nitrate + nitrite) levels are also found to be significantly decreased in cases with respect to controls (22.89 ± 2.65 umol/l vs. 24.73 ± 3.80 umol/l). Total oxidative stress is significantly increased in cases than in control subjects (23.34 ± 2.64 μmol H2O2 equiv./l vs. ± 21.43 ± 2.47 μmol H2O2 equiv/l). Vitamin C levels are also significantly decreased in cases as compared to controls (1.23 ± 0.25 mg/dl vs. 1.34 ± 0.28 mg/dl). Positive correlation between neonatal birth weight and maternal serum PON1 arylesterase activity (r = 0.682, p < 0.05) while negative correlation is obtained between neonatal birth weight and maternal serum oxidative stress (r = -0.478, p < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis is applied for assessing predictive utility which demonstrated a significant association of birth weight with PON1 arylesterase activity (AUC = 0.960, Naglekerke's R (2) = 0.793, p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Decreased arylesterase activity and antioxidant vitamin C levels with increased total oxidative stress in maternal serum may be considered as the additional risk factors for the development of low birth weight newborn.
Keywords: Arylesterase; Low birth weight; Total oxidative stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative status and serum PON1 activity in beta-thalassemia minor.Clin Biochem. 2007 Mar;40(5-6):287-91. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2006.10.028. Epub 2007 Jan 13. Clin Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17296173
-
Decreased serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities in patients with rosacea.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Feb;29(2):367-370. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12556. Epub 2014 May 22. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015. PMID: 24854673
-
Influence of single hemodialysis session on serum paraoxonase-1, arylesterase activity, total oxıdant status and total antioxidant status.Minerva Med. 2014 Feb;105(1):79-87. Minerva Med. 2014. PMID: 24572453
-
Evaluation of Serum Paraoxonase, Arylesterase, Prolidase Activities and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Alopecia Areata.Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2019;32(2):59-64. doi: 10.1159/000494690. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30544126
-
Serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activity and oxidative status in patients with multiple sclerosis.J Clin Neurosci. 2013 Aug;20(8):1106-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2012.09.020. Epub 2013 May 10. J Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23669169
Cited by
-
The impact of environmental and dietary exposure on gestational diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive review emphasizing the role of oxidative stress.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 2;16:1393883. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1393883. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40241987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muthayya S. Maternal nutrition and low birth weight—what is more important? IndianJ Med Res. 2009;130:600–608. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, tenth revision. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1992. - PubMed
-
- Park K. Park’s textbook of preventive and social medicine. 21. Jabalpur: M.S.Banarsidas Bhanot; 2011. p. 494.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous