Effects of teicoplanin on cell number of cultured cell lines
- PMID: 27486356
- PMCID: PMC4961922
- DOI: 10.1515/intox-2015-0004
Effects of teicoplanin on cell number of cultured cell lines
Abstract
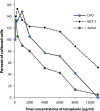
Teicoplanin is a glycopeptide antibiotic with a wide variation in human serum half-life. It is also a valuable alternative of vancomycin. There is however no study on its effect on cultured cells. The aim of the present study was to test the effect of teicoplanin on cultured cell lines CHO, Jurkat E6.1 and MCF-7. The cultured cells were exposed to teicoplanin at final concentrations of 0-11000 μg/ml for 24 hours. To determine cell viability, the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) test was performed. At low concentrations of teicoplanin the numbers of cultured cells (due to cell proliferation) were increased in the three cell lines examined. The maximum cell proliferation rates were observed at concentrations of 1000, 400, and 200 μg/ml of teicoplanin for CHO, MCF-7 and Jurkat cell lines, respectively. Cell toxicity was observed at final concentrations over 2000, 6000, and 400 μg/ml of teicoplanin for CHO, MCF-7 and Jurkat cell lines, respectively. A dose-dependent manner of cell toxicity was observed. Our present findings indicated that teicoplanin at clinically used concentrations induced cell proliferation. It should therefore be used cautiously, particularly in children, pregnant women and patients with cancer.
Keywords: MTT; human cell lines; proliferation; teicoplanin; toxicology.
Figures
References
-
- Eggleston M, Ofosu J. Teicoplanin, a new agent for gram positive bacterial infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1988;9:209–211. - PubMed
-
- Glupezynski Y, Lagast H, Auwera PV, Thys JP, Crokaert F, Yourassowsky E, Meunier-Carpentier F, Klastersky J, Kains JP, Serruys-Schoutens E. Clinical evaluation of teicoplanin for therapy of severe infections caused by Gram positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986;29:52–57. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guzek A, Korzeniewski K, Nitsch-Osuch A, Rybicki Z, Prokop E. In vitro susceptibility of staphylococci and enterococci to vancomycin and teicoplanin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;788:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Jovetic S, Zhu Y, Marcone GL, Marinelli F, Tramper J. β-Lactam and glycopeptide antibiotics: first and last line of defense? Trends in Biotechnol. 2010;28:596–604. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources