Exercise And Heart Failure: Advancing Knowledge And Improving Care
- PMID: 27486494
- PMCID: PMC4969018
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcj-12-2-110
Exercise And Heart Failure: Advancing Knowledge And Improving Care
Abstract
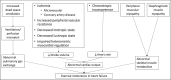
Exercise limitation is the hallmark of heart failure, and an increasing degree of intolerance is associated with poor prognosis. Objective evaluation of functional class (e.g., cardiopulmonary exercise testing) is essential for adequate prognostication in patients with advanced heart failure and for implementing an appropriate exercise training program. A graded exercise program has been shown to be beneficial in patients with heart failure and has become an essential component of comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation in these patients. An exercise program tailored to the patient's preferences, possibilities, and physiologic reserve has the greatest chance of being successful. Despite being safe, effective, and a guideline-recommended treatment to improve quality of life, exercise training remains grossly underutilized. Patient, physician, insurance and practice barriers need to be addressed to improve this quality gap.
Keywords: cardiopulmonary exercise testing; exercise; heart failure.
Figures

References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015 Jan 27;131(4):e29–322. - PubMed
-
- Katz AM. The “modern” view of heart failure: how did we get here? Circ Heart Fail. 2008 May;1(1):63–71. - PubMed
-
- Silverman ME. A view from the millennium: the practice of cardiology circa 1950 and thereafter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Apr;33(5):1141–51. - PubMed
-
- Wasserman K et al. Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Aug;35(2):236–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

