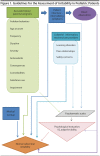
Irritability in Pediatric Patients: Normal or Not?
- PMID: 27486529
- PMCID: PMC4956414
- DOI: 10.4088/PCC.15br01893
Irritability in Pediatric Patients: Normal or Not?
Abstract
The goal of this article is to describe the concept of irritability in children and youth, which has been revisited in the DSM-5. Traditionally, this behavior has been more commonly associated with mood disorders, which may account for the rising incidence of bipolar disorder diagnosis and overuse of mood-stabilizing medications in pediatric patients. While not predictive of mania, persistent nonepisodic irritability, if undetected, may escalate to violent behavior with potentially serious outcomes. It is therefore important to educate clinicians about how to accurately assess irritability in pediatric patients.
Similar articles
-
Irritability in children and adolescents: past concepts, current debates, and future opportunities.Braz J Psychiatry. 2013;35 Suppl 1(0 1):S32-9. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2013-S107. Braz J Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24142126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different psychophysiological and behavioral responses elicited by frustration in pediatric bipolar disorder and severe mood dysregulation.Am J Psychiatry. 2007 Feb;164(2):309-17. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2007.164.2.309. Am J Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17267795
-
Assessment of irritability in school-aged children by pediatric, family practice, and psychiatric providers.Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr;25(2):333-345. doi: 10.1177/1359104519865591. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31353938
-
Prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar I disorder: review of diagnostic validation by Robins and Guze criteria.J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66 Suppl 7:21-8. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16124838 Review.
-
Parental diagnoses in youth with narrow phenotype bipolar disorder or severe mood dysregulation.Am J Psychiatry. 2007 Aug;164(8):1238-41. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06101619. Am J Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17671287
Cited by
-
Pediatric and adolescent mood disorders: An analysis of factors that influence inpatient presentation in the United States.Int J Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2022 Jun;9(2):89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpam.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Int J Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2022. PMID: 35663782 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder: current insights.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016 Aug 24;12:2115-24. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S100312. eCollection 2016. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016. PMID: 27601906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attention shifting in the context of emotional faces: Disentangling neural mechanisms of irritability from anxiety.Depress Anxiety. 2020 Jul;37(7):645-656. doi: 10.1002/da.23010. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Depress Anxiety. 2020. PMID: 32253797 Free PMC article.
-
Face Emotion Processing in Pediatric Irritability: Neural Mechanisms in a Sample Enriched for Irritability With Autism Spectrum Disorder.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020 Dec;59(12):1380-1391. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2019.09.002. Epub 2019 Sep 19. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31541675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Snaith RP, Taylor CM. Irritability: definition, assessment, and associated factors. Br J Psychiatry. 1985;147(2):127–136. - PubMed
-
- Leibenluft E, Blair RJ, Charney DS, et al. Irritability in pediatric mania and other childhood psychopathology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;1008(1):201–218. - PubMed
-
- Mayes SD, Mathiowetz C, Kokotovich C, et al. Stability of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder symptoms (irritable-angry mood and temper outbursts) throughout childhood and adolescence in a general population sample. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2015;43(8):1543–1549. - PubMed
-
- Judd LL, Schettler PJ, Coryell W, et al. Overt irritability/anger in unipolar major depressive episodes: past and current characteristics and implications for long-term course. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(11):1171–1180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical