Enterovirus D68 and Human Respiratory Infections
- PMID: 27486738
- PMCID: PMC7171721
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1584795
Enterovirus D68 and Human Respiratory Infections
Abstract
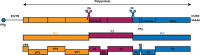
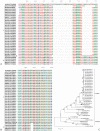
Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68) is a member of the species Enterovirus D in the genus Enterovirus of the Picornaviridae family. EV-D68 was first isolated in the United States in 1962 and is primarily an agent of respiratory disease. Infections with EV-D68 have been rarely reported until recently, when reports of EV-D68 associated with respiratory disease increased notably worldwide. An outbreak in 2014 in the United States, for example, involved more than 1,000 cases of severe respiratory disease that occurred across almost all states. Phylogenetic analysis of all EV-D68 sequences indicates that the circulating strains of EV-D68 can be classified into two lineages, lineage 1 and lineage 2. In contrast to the prototype Fermon strain, all circulating strains have deletions in their genomes. Respiratory illness associated with EV-D68 infection ranges from mild illness that just needs outpatient service to severe illness requiring intensive care and mechanical ventilation. To date, there are no specific medicines and vaccines to treat or prevent EV-D68 infection. This review provides a detailed overview about our current understanding of EV-D68-related virology, epidemiology and clinical syndromes, pathogenesis, and laboratory diagnostics.
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA.
Figures


References
-
- Schieble J H, Fox V L, Lennette E H. A probable new human picornavirus associated with respiratory diseases. Am J Epidemiol. 1967;85(2):297–310. - PubMed
-
- Ishiko H, Miura R, Shimada Y. et al.Human rhinovirus 87 identified as human enterovirus 68 by VP4-based molecular diagnosis. Intervirology. 2002;45(3):136–141. - PubMed
-
- Khetsuriani N Lamonte-Fowlkes A Oberst S Pallansch M A; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Enterovirus surveillance—United States, 1970-2005 MMWR Surveill Summ 20065581–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

