Home telemonitoring and remote feedback between clinic visits for asthma
- PMID: 27486836
- PMCID: PMC7433298
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011714.pub2
Home telemonitoring and remote feedback between clinic visits for asthma
Abstract
Background: Asthma is a chronic disease that causes reversible narrowing of the airways due to bronchoconstriction, inflammation and mucus production. Asthma continues to be associated with significant avoidable morbidity and mortality. Self management facilitated by a healthcare professional is important to keep symptoms controlled and to prevent exacerbations.Telephone and Internet technologies can now be used by patients to measure lung function and asthma symptoms at home. Patients can then share this information electronically with their healthcare provider, who can provide feedback between clinic visits. Technology can be used in this manner to improve health outcomes and prevent the need for emergency treatment for people with asthma and other long-term health conditions.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of home telemonitoring with healthcare professional feedback between clinic visits, compared with usual care.
Search methods: We identified trials from the Cochrane Airways Review Group Specialised Register (CAGR) up to May 2016. We also searched www.clinicaltrials.gov, the World Health Organization (WHO) trials portal and reference lists of other reviews, and we contacted trial authors to ask for additional information.
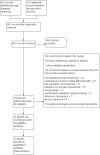
Selection criteria: We included parallel randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of adults or children with asthma in which any form of technology was used to measure and share asthma monitoring data with a healthcare provider between clinic visits, compared with other monitoring or usual care. We excluded trials in which technologies were used for monitoring with no input from a doctor or nurse. We included studies reported as full-text articles, those published as abstracts only and unpublished data.
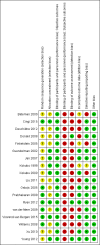
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors screened the search and independently extracted risk of bias and numerical data, resolving disagreements by consensus.We analysed dichotomous data as odds ratios (ORs) while using study participants as the unit of analysis, and continuous data as mean differences (MDs) while using random-effects models. We rated evidence for all outcomes using the GRADE (Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation Working Group) approach.
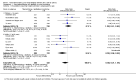
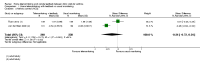
Main results: We found 18 studies including 2268 participants: 12 in adults, 5 in children and one in individuals from both age groups. Studies generally recruited people with mild to moderate persistent asthma and followed them for between three and 12 months. People in the intervention group were given one of a variety of technologies to record and share their symptoms (text messaging, Web systems or phone calls), compared with a group of people who received usual care or a control intervention.Evidence from these studies did not show clearly whether asthma telemonitoring with feedback from a healthcare professional increases or decreases the odds of exacerbations that require a course of oral steroids (OR 0.93, 95% confidence Interval (CI) 0.60 to 1.44; 466 participants; four studies), a visit to the emergency department (OR 0.75, 95% CI 0.36 to 1.58; 1018 participants; eight studies) or a stay in hospital (OR 0.56, 95% CI 0.21 to 1.49; 1042 participants; 10 studies) compared with usual care. Our confidence was limited by imprecision in all three primary outcomes. Evidence quality ratings ranged from moderate to very low. None of the studies recorded serious or non-serious adverse events separately from asthma exacerbations.Evidence for measures of asthma control was imprecise and inconsistent, revealing possible benefit over usual care for quality of life (MD 0.23, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.45; 796 participants; six studies; I(2) = 54%), but the effect was small and study results varied. Telemonitoring interventions may provide additional benefit for two measures of lung function.
Authors' conclusions: Current evidence does not support the widespread implementation of telemonitoring with healthcare provider feedback between asthma clinic visits. Studies have not yet proven that additional telemonitoring strategies lead to better symptom control or reduced need for oral steroids over usual asthma care, nor have they ruled out unintended harms. Investigators noted small benefits for quality of life, but these are subject to risk of bias, as the studies were unblinded. Similarly, some benefits for lung function are uncertain owing to possible attrition bias.Larger pragmatic studies in children and adults could better determine the real-world benefits of these interventions for preventing exacerbations and avoiding harms; it is difficult to generalise results from this review because benefits may be explained at least in part by the increased attention participants receive by taking part in clinical trials. Qualitative studies could inform future research by focusing on patient and provider preferences, or by identifying subgroups of patients who are more likely to attain benefit from closer monitoring, such as those who have frequent asthma attacks.
Conflict of interest statement
Kayleigh Kew: none.
Christopher Cates: none.
Figures


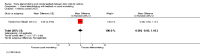


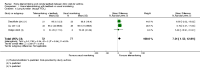


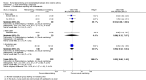


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bateman 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bateman ED, Kruger MJ. A computer‐based home‐monitoring disease management programme, Pulmassist Plus® (PAP), achieves significant improvement in quality of life, and healthcare costs in moderate and severe asthma [abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2000;161:A457.
Cingi 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cingi C, Yorgancioglu A, Cingi CC, Oguzulgen K, Muluk NB, Ulusoy, S, et al. The "physician on call patient engagement trial" (POPET): measuring the impact of a mobile patient engagement application on health outcomes and quality of life in allergic rhinitis and asthma patients. International Forum of Allergy and Rhinology 2015;5(6):487‐97. - PubMed
Deschildre 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Deschildre A, Beghin L, Salleron J, Iliescu C, Thumerelle C, Santos C, et al. Home telemonitoring (forced expiratory volume in 1 s) in children with severe asthma does not reduce exacerbations. European Respiratory Journal 2012;39:290‐6. - PubMed
Donald 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Donald KJ, McBurney H, Teichtahl H, Irving L. A pilot study of telephone based asthma management. Australian Family Physician 2008;37:170‐3. - PubMed
Finkelstein 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Finkelstein J. Inhaled steroid adherence in moderate and severe asthma. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 2000; Vol. 31/07/2005 End date.
-
- Finkelstein J, Joshi A, Amelung P. Evaluation of home telemanagement in adult asthma patients [Abstract]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2005;115(2):S63.
-
- Finkelstein J, Joshi A, Arora M, Amelung P. Impact of home telemanagement in adult asthma [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society 2005 International Conference. 2005 May 20‐25; San Diego:[A40] [Poster: G14].
Guendelman 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Guendelman S, Meade K, Benson M, Chen YQ, Samuels S. Improving asthma outcomes and self‐management behaviors of inner‐city children: a randomized trial of the Health Buddy interactive device and an asthma diary. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2002;156:114‐20. - PubMed
-
- Guendelman S, Meade K, Chen YQ, Benson M. Asthma control and hospitalizations among inner‐city children: results of a randomized trial. Telemedicine Journal and e‐Health 2004;10(Suppl 2):S6‐14. - PubMed
Jan 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Jan RL, Wang JY, Huang MC, Tseng SM, Su HJ, Liu LF, et al. An internet‐based interactive tele‐monitoring system for improving childhood asthma outcomes in Taiwan. Telemedicine Journal and e‐Health 2007;13:257‐68. - PubMed
Kokubu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kokubu F, Suzuki H, Sano Y, Kihara N, Adachi M. [Tele‐medicine system for high‐risk asthmatic patients]. Arerugi [Allergy] 1999;48:700‐12. - PubMed
Kokubu 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kokubu F, Nakajima S, Ito K, Makino S, Kitamura S, Fukuchi Y, et al. [Hospitalization reduction by an asthma tele‐medicine system]. Arerugi [Allergy] 2000;49:19‐31. - PubMed
Liu 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Liu WT, Huang CD, Wang CH, Lee KY, Lin SM, Kuo HP. A mobile telephone‐based interactive self‐care system improves asthma control. European Respiratory Journal 2011;37:310‐7. - PubMed
-
- Liu WT, Wang CH, Huang CD, Kuo HP, Liu WT, Kuo HP. A novel mobile phone‐based self‐care system improves asthma control [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society International Conference. 2007 May 18‐23; San Francisco:[A93].
Ostojic 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ostojic V, Cvoriscec B, Ostojic SB, Reznikoff D, Stipic‐Markovic A, Tudjman Z. Improving asthma control through telemedicine: a study of short‐message service. Telemedicine Journal and e‐Health 2005;11:28‐35. - PubMed
-
- Ostojic V, Cvoriscec B, Ostojic SB, Tudjman Z, Stipic‐Markovic A. Using of short message service (SMS) for long‐term management of asthmatic patients [abstract]. European Respiratory Society 12th Annual Congress. 2002 Sep 14‐18; Stockholm:[P1003].
Prabhakaran 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Prabhakaran L, Chee J, Chua KC, Mun WW. The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a study of short message service (SMS) [Abstract]. Respirology (Carlton, Vic.) 2009;14:A217 [PD 10‐01].
-
- Prabhakaran L, Chee WY, Chua KC, Abisheganaden J, Wong WM. The use of text messaging to improve asthma control: a pilot study using the mobile phone short messaging service (SMS). Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2010;16:286‐90. - PubMed
Ryan 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ryan D, Pinnock H, Amanda L, Lionel T, Sheikh A, Musgrave S, et al. Can mobile phone technology improve asthma control? A randomised trial [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society 20th Annual Congress. 2010 Sep 18‐22; Barcelona:[2138].
-
- Ryan D, Pinnock H, Lee AJ, Tarassenko L, Ayansina D, Musgrave S, et al. Can your mobile phone help your asthma: preliminary results [Abstract]. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2010;19:A15 [54].
-
- Ryan D, Pinnock H, Lee AJ, Tarassenko L, Pagliari C, Sheikh A, et al. The CYMPLA trial. Mobile phone‐based structured intervention to achieve asthma control in patients with uncontrolled persistent asthma: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2009;18:343‐5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ryan D, Pinnock H, Tarassenko L, Lee A, Sheikh A, Price D. Can your mobile phone improve your asthma? [Abstract]. Thorax 2010;65:S135.
van der Meer 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Meer V, Bakker MJ, Hout WB, Rabe KF, Sterk PJ, Kievit J, et al. Self‐management for asthma on the Internet: a randomized study. Nederlands Tijdschrift Voor Geneeskunde 2010;154:403‐9.
-
- Meer V, Stel HF, Bakker MJ, Roldaan AC, Assendelft WJJ, Sterk PJ, et al. Internet‐based self management improves short‐term asthma control: the SMASHING study [Abstract]. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2008;17:124.
-
- Meer V, Bakker MJ, Rabe KF, Sterk PJ, Kievit J, Assendelft WJJ, et al. Improved quality of life by internet based self management versus usual care in asthma a randomized controlled trial [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society 18th Annual Congress. 2008 Oct 3‐7; Berlin:[1372].
-
- Meer V, Bakker MJ, Hout WB, Rabe KF, Sterk PJ, Kievit J, et al. Internet‐based self‐management plus education compared with usual care in asthma: a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2009;151:110‐20. - PubMed
Voorend‐van Bergen 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Beerthuizen T, Voorend‐van Bergen S, Hout WB, Vaessen‐Verberne AA, Brackel HJ, Landstra AM, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of FENO‐based and web‐based monitoring in paediatric asthma management: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2016;71(7):607‐13. [CENTRAL: 1139864; CRS: 4900132000017696; PUBMED: 27048197] - PubMed
-
- Bergen SV, Beerthuizen T, Hout W, Vaessen‐Verberne A, Brackel H, Landstra A, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of FeNO‐ and web‐based monitoring in pediatric asthma management. European Respiratory Journal 2015;46(Suppl 59):OA4776. [CENTRAL: 1126623; CRS: 4900132000012681; EMBASE: 72107805]
-
- Voorend‐van Bergen S, Vaessen‐Verberne A, Landstra A, Brackel H, Berg N, Jongste J, et al. FeNO and web‐based monitoring in paediatric asthma management; the BATMAN study [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2013;42(Suppl 57):629s [3014].
-
- Voorend‐van Bergen S, Vaessen‐Verberne AA, Brackel HJ, Landstra AM, Berg NJ, Hop WC, et al. Monitoring strategies in children with asthma: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2015;70(6):543‐50. - PubMed
Willems 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- NCT00411346. Patient Research In Self‐Management of Asthma (PRISMA). https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00411346 (accessed 2 June 2015).
-
- Willems DC, Joore MA, Hendriks JJ, Nieman FH, Severens JL, Wouters EF, et al. The effectiveness of nurse‐led telemonitoring of asthma: results of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 2008;14:600‐9. - PubMed
-
- Willems DC, Joore MA, Hendriks JJ, Duurling RA, Wouters EF, Severens JL. Process evaluation of a nurse‐led telemonitoring programme for patients with asthma. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2007;13:310‐7. - PubMed
Xu 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- ACTRN12606000400561. Improving Childhood Asthma Management Through a Telemedicine Monitoring Network. https://www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=1260... (accessed 2 June 2015).
-
- Xu C, Jackson M, Scuffham PA, Wootton R, Simpson P, Whitty J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of an interactive voice response telephone system and specialist nurse support for childhood asthma management. Journal of Asthma 2010;47:768‐73. - PubMed
Young 2012 {published and unpublished data}
References to studies excluded from this review
Aaron 2016 {published data only}
-
- Aaron M, Nelson BW, Kaltsas E, Brown RW, Thomas LJ, Patel MR. Impact of goal setting and goal attainment methods on asthma outcomes: findings from an asthma self‐management intervention for African American women. Health Education & Behavior 2016;[Epub ahead of print]. [CRS: 4900132000021647; PUBMED: 27179290] - PMC - PubMed
Andersen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Andersen UM. Does a www‐based interactive computer program change asthma outcomes, quality of life and asthma knowledge [Abstract]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2007;119:S9 [34].
Apter 2000 {published data only}
-
- Apter A. Inhaled steroid adherence in moderate and severe asthma. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 2000; Vol. 31/08/2005 End date.
Apter 2015 {published data only}
-
- Apter AJ, Bryant‐Stephens, Morales KH, Wan F, Hardy S, Reed‐Wells S, et al. Using IT to improve access, communication, and asthma in African American and Hispanic/Latino adults: rationale, design, and methods of a randomized controlled trial. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2015;44:119‐28. - PubMed
Araujo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Araujo L, Jacinto T, Moreira A, Castel‐Branco MG, Delgado L, Costa‐Pereira A, et al. Clinical efficacy of web‐based versus standard asthma self‐management. Journal of Investigational Allergology and Clinical Immunology 2012;22:28‐34. - PubMed
Baptist 2013 {published data only}
-
- Baptist AP, Ross JA, Yang Y, Song PX, Clark NM. A randomized controlled trial of a self‐regulation intervention for older adults with asthma. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2013;61:747‐53. - PubMed
Barbanel 2003 {published data only}
Bender 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bender BG. Assessment mode and validity of self‐reports in children. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 2001; Vol. 31/01/2005 End date.
Bender 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bender BG, Bartlett SJ, Rand CS, Turner C, Wamboldt FS, Zhang L. Impact of interview mode on accuracy of child and parent report of adherence with asthma‐controller medication. Pediatrics 2007;120:e471‐7. - PubMed
Bender 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bender BG, Apter A, Bogen DK, Dickinson P, Fisher L, Wamboldt FS, et al. Test of an interactive voice response intervention to improve adherence to controller medications in adults with asthma. Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine 2010;23:159‐65. - PubMed
Boyd 2014 {published data only}
-
- Boyd MJ, Elliott RA, Barber N, Mehta R, Waring J, Chuter A, et al. The impact of the New Medicines Service (NMS) in England on patients' adherence to their medicines. International Journal of Pharmacy Practice 2014;22(S2):66.
Burbank 2012 {published data only}
-
- Burbank A, Rettiganti M, Brown RH, Jones S, Perry TT. Asthma education via telemedicine: effects on asthma knowledge and self‐efficacy [Abstract]. Journal of Investigative Medicine 2012;60:401.
Burkhart 2002 {published data only}
-
- Burkhart P. Promoting children's adherence to asthma self‐management. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 2002; Vol. 31/07/2004 End date.
Bynum 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bynum A, Hopkins D, Thomas A, Copeland N, Irwin C. The effect of telepharmacy counseling on metered‐dose inhaler technique among adolescents with asthma in rural Arkansas. Telemedicine Journal and e‐Health 2001;7:207‐17. - PubMed
Chan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Callahan CW. Asthma In‐Home Monitoring (AIM) Trial. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct/show/NCT00282516 (accessed 4 August 2015).
-
- Callahan CW, Chan DS, Hatch‐Pigott G, Manning N, Proffitt L, Lawless A, et al. One year randomized controlled trial of home telemonitoring of children with persistent asthma using store‐and‐forward technology vs office‐based care [abstract]. American Thoracic Society 2005 International Conference. 2005 May 20‐25; San Diego:[C47] [Poster: A21].
-
- Chan DS, Callahan CW, Hatch‐Pigott VB, Lawless A, Proffitt HL, Manning NE, et al. Internet‐based home monitoring and education of children with asthma is comparable to ideal office‐based care: results of a 1‐year asthma in‐home monitoring trial. Pediatrics 2007;119:569‐78. - PubMed
-
- Chan DS, Callahan CW, Sheets SJ, Moreno CN, Malone FJ. An Internet‐based store‐and‐forward video home telehealth system for improving asthma outcomes in children. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 2003;60:1976‐81. - PubMed
Chandler 1990 {published data only}
-
- Chandler MH, Clifton GD, Louis BA, Coons SJ, Foster TS, Phillips BA. Home monitoring of theophylline levels: a novel therapeutic approach. Pharmacotherapy 1990;10:294‐300. - PubMed
Chatkin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chatkin JM, Blanco DC, Scaglia N, Wagner MB, Fritscher CC, Chatkin J, et al. Impact of a low‐cost and simple intervention in enhancing treatment adherence in a Brazilian asthma sample. Journal of Asthma 2006;43:263‐6. - PubMed
Chen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Chen SH, Huang JL, Yeh KW, Tsai YF. Interactive support interventions for caregivers of asthmatic children. Journal of Asthma 2013;50:649‐57. - PubMed
Cicutto 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cicutto L, Ashby MN, Feldman D. Telephone intervention based strategies to increase the completion and use of asthma action plans for adults with asthma [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society International Conference. 2009 May 15‐20; San Diego:A1033.
Clark 2007 {published data only}
-
- Clark NM, Gong ZM, Wang SJ, Lin X, Bria WF, Johnson TR, et al. A randomized trial of a self‐regulation intervention for women with asthma. Chest 2007;132:88‐97. - PubMed
Clarke 2014 {published data only}
-
- Clarke SA, Calam R, Morawska A, Sanders M. Developing web‐based Triple P 'Positive Parenting Programme' for families of children with asthma. Child 2014;40:492‐7. - PubMed
Claus 2004 {published data only}
-
- Claus R, Michael H, Josef L, Jan‐Torsten T, Marion S. Internet based patient education evaluation of a new tool for young asthmatics [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society 14th Annual Congress. 2004 Sep 3‐7; Glasgow; Vol. 24:383s.
Cruz‐Correia 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cruz‐Correia R, Fonseca J, Lima L, Araujo L, Delgado L, Castel‐Branco MG, et al. A comparison of web‐based and paper‐based self management tools for asthma: patients' opinions and quality of data in a randomised crossover study. Journal on Information Technology in Healthcare 2007;5:357‐71. - PubMed
-
- Cruz‐Correia R, Fonseca J, Lima L, Araújo L, Delgado L, Castel‐Branco MG, et al. Web‐based or paper‐based self‐management tools for asthma ‐ patients' opinions and quality of data in a randomized crossover study. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 2007;127:178‐89. - PubMed
de Jongste 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jongste JC, Carroro S, Hop WC, Baraldi E. Daily exhaled nitric oxide telemonitoring in the management of childhood asthma [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society International Conference. 2008 May 16‐21; Toronto:Poster #908.
De Vera 2014 {published data only}
Dwinger 2013 {published data only}
Eakin 2012 {published data only}
Fonseca 2006 {published data only}
-
- Fonseca JA, Costa‐Pereira A, Delgado L, Fernandes L, Castel‐Branco MG. Asthma patients are willing to use mobile and web technologies to support self‐management. Allergy 2006;61:389‐90. - PubMed
Foster 2014 {published data only}
-
- Foster J, Smith L, Usherwood T, Sawyer S, Reddel H. Electronic reminders improve adherence with preventer inhalers in Australian primary care patients [Abstract]. Annual Scientific Meetings of the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Australian and New Zealand Society of Respiratory Science. 2014 April 4‐9; Adelaide:24 [TO 034].
Friedman 1999 {published data only}
-
- Friedman R. Impact of a telecommunication system in childhood asthma. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 1999; Vol. 29/09/2004 End date.
Garbutt 2010 {published data only}
-
- Garbutt JM, Banister C, Highstein G, Sterkel R, Epstein J, Bruns J, et al. Telephone coaching for parents of children with asthma: impact and lessons learned. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2010;164:625‐30. - PubMed
-
- Swerczek LM, Banister C, Bloomberg GR, Bruns JM, Epstein J, Highstein GR, et al. A telephone coaching intervention to improve asthma self‐management behaviors. Pediatric Nursing 2013;39:125‐30, 145. - PubMed
Gruffydd‐Jones 2005 {published data only}
Gustafson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gustafson D, Wise M, Bhattacharya A, Pulvermacher A, Shanovich K, Phillips B, et al. The effects of combining web‐based eHealth with telephone nurse case management for pediatric asthma control: a randomized controlled trial. [References]. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2012;14:41‐59. - PMC - PubMed
Halterman 2012 {published data only}
Hashimoto 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hashimoto S, Brinke A, Roldaan AC, Veen IH, Möller GM, Sont JK, et al. Internet‐based tapering of oral corticosteroids in severe asthma: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2011;66:514‐20. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto S, Brinke A, Roldaan AC, Veen IH, Moller GM, Sont JK, et al. Monitoring exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) to tailor the lowest effective dose of oral corticosteroids in severe asthma (MONOSA‐study) [Abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2010;181:A3721.
Huang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Huang JL, Chen SH, Yeh KW. Health outcomes, education, healthcare delivery and quality [3056]. Constructed supporting program improves asthma treatment outcomes in children. World Allergy Organization Journal 2013;6:P224.
Janevic 2012 {published data only}
Jerant 2003 {published data only}
-
- Jerant A. A randomized trial of home self‐efficacy enhancement. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 2003; Vol. 31/12/2007 End date.
Kattan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kattan M, Crain EF, Steinbach S, Visness CM, Walter M, Stout JW, et al. A randomized clinical trial of clinician feedback to improve quality of care for inner‐city children with asthma. Pediatrics 2006;117:e1095‐103. - PubMed
Khan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Khan MSR, O'Meara M, Stevermuer TL, Henry RL. Randomized controlled trial of asthma education after discharge from an emergency department. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2004;40:674‐7. - PubMed
-
- Khan S, O'Meara M, Hurst T, Henry RL. Randomised controlled trial of asthma education by telephone after discharge from an emergency department [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2003;22:Abstract No: [P2294].
Kojima 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kojima N, Takeda Y, Akashi M, Kamiya T, Matsumoto M, Ohya Y, et al. Interactive education during summer camp for children with asthma improved adherence of self‐management [Abstract]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2005;115:S115.
Lam 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lam A. Practice innovations: delivering medication therapy management services via videoconference interviews. Consultant Pharmacist 2011;26:764‐74. - PubMed
Lobach 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lobach DF, Kawamoto K, Anstrom KJ, Silvey GM, Willis JM, Johnson FS, et al. A randomized trial of population‐based clinical decision support to manage health and resource use for Medicaid beneficiaries. Journal of Medical Systems 2013;37:9922. - PubMed
MacDonell 2015 {published data only}
-
- MacDonell KK, Gibson‐Scipio WM, Lam P, Naar‐King S, Secord E. The Detroit young adult asthma project: feasibility and acceptability of a multi‐component, technology‐based intervention targeting adherence to controller medication. American Thoracic Society International Conference. 2015 May 15‐20; Denver:A3634.
McCowan 2001 {published data only}
-
- McCowan C, Neville RG, Ricketts IW, Warner FC, Hoskins G, Thomas GE. Computer assisted assessment and management of patients with asthma. American Thoracic Society 97th International Conference. 2001 May 18‐23; San Francisco.
McPherson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Glazebrook C, McPherson A, Forster D, James C, Crook I, Smyth A. The asthma files: randomised controlled trial of interactive multimedia program to promote self‐management skills in children [abstract]. American Thoracic Society 100th International Conference. 2004 May 21‐26; Orlando:D92 Poster 506.
-
- McPherson AC, Glazebrook C, Forster D, James C, Smyth A. A randomized, controlled trial of an interactive educational computer package for children with asthma. Pediatrics 2006;117:1046‐54. - PubMed
Merchant 2016 {published data only}
-
- Merchant R, Inamdar R, Quade R, Sickle D, Maenner M, Patmas M. Interim results from a randomized, controlled trial of remote monitoring of inhaled bronchodilator use on asthma control and management [Abstract]. American College of Chest Physicians Annual Meeting. 26‐31 October 2013; Chicago; Vol. 144:71A.
-
- Merchant RK, Inamdar R, Quade RC. Effectiveness of population health management using the propeller health asthma platform: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2016;4(3):455‐63. [CENTRAL: 1135189; CRS: 4900132000015067; PUBMED: 26778246] - PubMed
Morrison 2014 {published data only}
Murphy 2001 {published data only}
-
- Murphy JC. Telemedicine offers new way to manage asthma. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 2001;58:1693, 1696. - PubMed
NCT00149474 {published data only}
-
- Peak Flow Monitoring in Older Adults With Asthma. https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00149474 (accessed 2 June 2015).
NCT00562081 {published data only}
-
- The Virtual Asthma Clinic. https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00562081 (accessed 2 June 2015).
NCT00910585 {published data only}
-
- Coaching in Childhood Asthma. https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00910585 (accessed 2 June 2015).
NCT00964301 {published data only}
-
- Telemedicine Education for Rural Children With Asthma. https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00964301 (accessed 2 June 2015).
NCT01117805 {published data only}
-
- Women of Color and Asthma Control. https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT01117805 (accessed 2 June 2015).
Osman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Osman L. A controlled study evaluating relative benefits of two types of review after an A&E attendance. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 1997; Vol. 01/03/2001 End date.
-
- Osman L. A randomised controlled trial of benefits of specialist review or telephone follow up after an Accident & Emergency attendance for asthma. http://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN11122844 (accessed 4 August 2015).
Pedram 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pedram RS, Piroozmand N, Zolfaghari M, Kazemnejad A, Firoozbakhsh S. Education of how‐to‐use peak flow meter and following up via SMS on asthma self‐management [Farsi]. HAYAT 2012;18:1‐9.
Peruccio 2005 {published data only}
-
- Peruccio D, Bauer B, Delaronde S. Improving asthma treatment and quality of life in a managed care population [Abstract]. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2005;115:S63. - PubMed
Petrie 2012 {published data only}
-
- Petrie KJ, Perry K, Broadbent E, Weinman J. A text message programme designed to modify patients' illness and treatment beliefs improves self‐reported adherence to asthma preventer medication. British Journal of Health Psychology 2012;17:74‐84. - PubMed
Pinnock 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pinnock H, Sheikh A, Bawden R, Proctor S, Wolfe S, Scullion J, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing telephone review with fact to face consultations in the management fo adult asthmatics in UK primary care. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2002;11:68‐9.
-
- Pinnock H, Sheikh A, Bawden R, Proctor S, Wolfe S, Scullion J, et al. Cost effectiveness of telephone vs face to face consultations for annual asthma review: randomised controlled trial in UK primary care [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2003;22:Abstract No: [2250].
-
- Pinnock H, Sheikh A, Bawden R, Proctor S, Wolfe S, Scullion J, et al. Telephone vs. face to face consultations in the management of adult asthmatics in UK primary care: a randomised controlled trial [abstract]. European Respiratory Society 12th Annual Congress. 2002 Sep 14‐18; Stockholm:Abstract no.: P593.
Pinnock 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pinnock H, Adlem L, Gaskin S, Snellgrove C, Harris J, Sheikh A. Impact on access of providing a telephone option for primary care asthma reviews: controlled implementation study [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2005;26:Abstract No. 1711.
-
- Pinnock H, Norman C, Bowden K, Sheikh A. Impact on asthma morbidity and patient enablement of providing a telephone option for primary care asthma reviews: phase IV controlled implementation study [Abstract]. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2006;15:187.
Price 2007 {published data only}
-
- Price D. A validation of the UK English language Asthma Control Test (ACT) for internet use among adults with asthma. East Norfolk and Waveney Research Consortium (Norfolk & Norwich UH/ Norwich PCT/James Paget/NWMHP) 2007; Vol. 1/1/2008:Ongoing.
-
- Price D. Validating asthma control test on the Internet. Suffolk and Norfolk Research and Development Consortium (S.A.N.D.) 2007; Vol. 30/12/2007:Ongoing.
Raat 2007 {published data only}
Rand 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rand C. Assessment Mode and Validity of Self‐Reports in Adults. clinicaltrials.gov (accessed 4 August 2015).
-
- Rand CS. Adherence intervention for minority children with asthma. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 2000; Vol. 31/03/2005 End date.
Rasmussen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Phanareth K, Rasmussen L, Nolte H, Backer V. Using the Internet as a tool for the management of asthma disease. European Respiratory Journal 2002;20:54s.
-
- Rasmussen L, Backer V, Phanareth K. Preliminary data from a clinical trial: does use of an internet based asthma‐monitoring tool increase lung function and asthma control? [abstract]. American Thoracic Society 99th International Conference. 2003 May 16‐21; Seattle:A102 Poster D6.
-
- Rasmussen L, Phanareth K, Nolte H, Backer V. A long term randomized clinical study of 300 asthmatics. An internet based asthma monitoring tool improves quality of life significantly [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2004;24:261s.
-
- Rasmussen L, Phanareth K, Nolte H, Backer V. Preliminary data from a clinical trial: an Internet based asthma monitoring tool increases lung function and decrease airway hyperresponsiveness [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2003;22:Abstract No: [3351].
-
- Rasmussen LM, Phanareth K, Nolte H, Backer V. Can internet‐based management improve asthma control? A long term randomised clinical study of 300 asthmatics [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2005;26:Abstract No. 400.
Rikkers‐Mutsaerts 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rikkers‐Mutsaerts E, Winters AE, Bakker MJ, Stel HF, Meer V, Jongste JC, et al. Internet‐based self‐management compared with usual care in adolescents with asthma: a randomised controlled trial [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society 20th Annual Congress. 2010 Sep 18‐22; Barcelona:[5396].
-
- Rikkers‐Mutsaerts ER, Winters AE, Bakker MJ, Stel HF, Meer V, Jongste JC, et al. Internet‐based self‐management compared with usual care in adolescents with asthma: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Pulmonology 2012;47:1170‐9. - PubMed
Rosenzweig 2008 {published data only}
-
- Rosenzweig JC, Williams AE, Kite A, Yang M, Kosinski M. Reliabilty and validity of the asthma control test (ACT) paper and telephone formats [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society 18th Annual Congress. 2008 Oct 3‐7; Berlin:[P3501].
Schatz 2003 {published data only}
-
- Schatz M, Rodriguez E, Falkoff R, Zeiger RS. The relationship of frequency of follow‐up visits to asthma outcomes in patients with moderate persistent asthma. Journal of Asthma 2003;40:49‐53. - PubMed
Schatz 2010 {published data only}
-
- Schatz M, Zeiger RS. Ineffectiveness of telephone‐based environmental control intervention to improve asthma outcomes. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2010;126:873‐5. - PubMed
Searing 2012 {published data only}
-
- Searing DA, Bender BG. Short message service (SMS) for asthma management: a pilot study utilizing text messaging to promote asthma self‐management [Abstract]. Annual Meeting of American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI). 2012 Mar 2‐6; Orlando; Vol. 129:AB142 [538].
Seid 2012 {published data only}
Shanovich 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shanovich KK, Pulvermacher AD, Hollman SJ, Richardson PA, Wise ME, Lee SH, et al. Nurse case management services provided to supplement a web‐based asthma education program [Abstract]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2008;121:S40 [155].
-
- Shanovich KK, Sorkness CA, Wise ME, Pulvermacher AD, Bhattacharya A, Gustafson DH. Internet telehealth for pediatric nurse case management improves asthma control [Abstract]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2009;123:S43.
Sparrow 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sparrow D. Telecommunications System in Asthma. www.clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00232557 (accessed 4 August 2015).
Taitel 2014 {published data only}
-
- Taitel M, Jiang JZ, Rudkin K. Impact of pharmacist‐call intervention program on new‐to‐therapy patients' medication adherence. Value in Health 2014;17:A138‐9.
Uysal 2013 {published data only}
-
- Uysal MA, Mungan D, Yorgancioglu A, Yildiz F, Akgun M, Gemicioglu B, et al. Asthma control test via text messaging: could it be a tool for evaluating asthma control?. Journal of Asthma 2013;50:1083‐9. - PubMed
van den Berg 2002 {published data only}
-
- Berg NJ, Have WH, Bindels PJE, Palen J, Aalderen WMC. Is the availability of a 24 hour asthma‐telephone useful in the implementation of asthma treatment guidelines for children aged 6‐16 years, among general practitioners? [abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2002;20:329s.
van Gaalen 2012 {published data only}
van Reisen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Reisen PAJ, Redelijkheid WG, Gaalen JL, Meer V, Bakker MJ, Beerthuizen T, et al. The long‐term outcomes of a one‐year Internet‐based self‐management support programme compared with usual care in asthma. Additional follow‐up 1.5 year after a randomized trial [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society 20th Annual Congress. 2010 Sep 18‐22; Barcelona:[E2160].
Vasbinder 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vasbinder E, Goossens L, Janssens H, Winter B, Dijk L, Vulto A, et al. E‐monitoring of asthma therapy to improve compliance in children (E‐MATIC). European Respiratory Journal 2015;46(Suppl 59):OA4771. [CENTRAL: 1126624; CRS: 4900132000015170; EMBASE: 72107800]
-
- Vasbinder EC, Goossens LMA, Janssens H, Winter BCM, Dijk L, Vulto AG, et al. E‐Monitoring of asthma therapy to improve compliance in children (E‐MATIC). Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety 2015;24:489. [CENTRAL: 1126710; CRS: 4900132000012210; EMBASE: 72098979]
-
- Vasbinder EC, Janssens HM, Rutten‐van Molken MP, Dijk L, Winter BC, Groot RC, et al. e‐Monitoring of asthma therapy to improve compliance in children using a real‐time medication monitoring system (RTMM): the e‐MATIC study protocol. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 2013;13:38. - PMC - PubMed
Vollmer 2006 {published data only}
-
- Vollmer WM, Kirshner M, Peters D, Drane A, Stibolt T, Hickey T, et al. Use and impact of an automated telephone outreach system for asthma in a managed care setting. American Journal of Managed Care 2006;12:725‐33. - PubMed
-
- Vollmer WM, Peters D, Kirshner M, Naleway A, Buist AS, Hickey T, et al. Use of a telephone triage system for asthma management [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society International Conference. 2005 May 20‐25; San Diego:[A40] [Poster: G15].
Wiecha 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wiecha JM, Adams WG. BostonBreathes: an RCT to improve pediatric asthma care with a home‐based interactive website for patient education, monitoring, and clinical teamwork. AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings. 2007:1154. - PubMed
Yun 2013 {published data only}
-
- Yun TJ, Arriaga RI. A text message a day keeps the pulmonologist away. Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2013:1769‐78.
Zachgo 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zachgo W, Juenemann R, Halbich C, Hofmann N, Eleljanova S, Reiss Plagemann C, et al. Optimized computer‐based inhaled steroid therapy in asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165:A766.
Zairina 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zairina E, Abramson M, Stewart K, Mcdonald C, Walker S, Rochford P, et al. Management of asthma with supportive telehealth of respiratory function in pregnancy (the mastery trial). Respirology 2015;20(Suppl 2):135. - PubMed
-
- Zairina E, Abramson MJ, McDonald CF, Li J, Dharmasiri T, Stewart K, et al. Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of a telehealth program ‐ management of asthma with supportive telehealth of respiratory function in pregnancy. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2015;15(1):84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zairina E, Abramson MJ, McDonald CF, Li J, Dharmasiri T, Stewart K, et al. Telehealth to improve asthma control in pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial. Respirology (Carlton, Vic.) 2016;21(5):867‐74. [CENTRAL: 1139850; CRS: 4900132000017642; PUBMED: 27037722] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ricci 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ricci A, Barosi G, Gelmetti A, Esposito R, Tzialla C, Napoli A, et al. A system of teleassistance for in‐house monitoring respiratory function in children with bronchial asthma. Minerva Pediatrica 2001;53:466‐7. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Ahmed 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ahmed S, Bartlett SJ, Ernst P, Lin CJ, Pare G, Perreault R, et al. My asthma portal: preliminary results of a web‐based self management intervention [Abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2011;183:A5321.
Perry 2015 {published data only}
-
- Perry TT, Halterman JS, Brown RH, Hunter CR, Randle SM, Tilford JM, et al. Breath connection: a school‐based telemedicine program for rural children with asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2015;135(2 Suppl 1):AB169.
Additional references
Atherton 2012
Australian Government Department of Health 2016
-
- Australian Government Department of Health. Telehealth Pilots Programme. http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/ehealth‐nb... (accessed 7 June 2016).
BTS/SIGN 2014
-
- British Thoracic Society/Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. British guideline on the management of asthma. https://www.brit‐thoracic.org.uk/guidelines‐and‐quality‐standards/asthma‐guideline/ (accessed 12 March 2015).
Cash‐Gibson 2012
Craven 2015
-
- Craven VE, Morton RW, Spencer S, Devadason SG, Everard ML. Electronic monitoring and reminding devices for improving adherence to inhaled therapy in patients with asthma. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011554] - DOI
de Jongh 2012
Gibson 2002
GINA 2014
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. www.ginaasthma.org/local/uploads/files/GINA_Report_2014_Aug12.pdf (accessed 12 March 2015).
Global Asthma Report 2011
-
- International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. The Global Asthma Report 2011. http://theunion.org/what‐we‐do/publications/technical/global‐asthma‐report (accessed 12 March 2015).
Government of the Netherlands 2016
-
- Government of the Netherlands. Government encouraging use of eHealth. https://www.government.nl/topics/ehealth/contents/government‐encouraging... (accessed 7 June 2016).
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime Inc). GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool. Ontario: McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime Inc), 2015.
Gurol‐Urganci 2013
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jaana 2009
-
- Jaan M, Paré G, Sicotte C. Home telemonitoring for respiratory conditions: a systematic review. American Journal of Managed Care 2009;15(5):313‐20. - PubMed
Jannett 2003
-
- Jennett PA, Affleck Hall L, Hailey D, Ohinmaa A, Anderson C, Thomas R, et al. The socio‐economic impact of telehealth: a systematic review. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2003;9(6):311‐20. - PubMed
Kew 2016
Laver 2013
Lustig 2012
-
- Lustig TA, Board on Health Care Services, Institute of Medicine. The Role of Telehealth in an Evolving Health Care Environment: Workshop Summary. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2012. - PubMed
McLean 2010
McLean 2011
Mclean 2013
Medicaid 2016
-
- Medicaid.gov. Delivery systems: telemedicine. https://www.medicaid.gov/medicaid‐chip‐program‐information/by‐topics/del... (accessed 7 June 2016).
Moher 2009
NRAD 2014
-
- Royal College of Physicians. Why asthma still kills: the national review of asthma deaths. https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/sites/default/files/why‐asthma‐still‐kills‐f... (accessed 12 March 2015).
Pinnock 2007a
-
- Pinnock H, Slack R, Pagliari C, Price D, Sheikh A. Understanding the potential role of mobile phone‐based monitoring on asthma self‐management: qualitative study. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 2007;37:794‐802. - PubMed
Rada 2015
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Steventon 2012
UK Department of Health 2012
-
- Department of Health. Long Term Conditions Compendium of Information: Third Edition (2012). https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/long‐term‐conditions‐compendi... (accessed 12 March 2015).
UK Department of Health 2013
-
- Department of Health. A mandate from the Government to the NHS Commisioning Board: April 2013 to March 2015. https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/fil... (accessed 12 March 2015).
Zhao 2014
-
- Zhao J, Zhai YK, Zhu WJ, Sun DX. Effectiveness of telemedicine for controlling asthma symptoms: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Telemedicine Journal and e‐Health 2014;21(6):484‐92. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Kew 2015
-
- Kew KM, Cates C. Asthma monitoring with remote feedback from a health professional. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 5. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011714] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

