IABP: history-evolution-pathophysiology-indications: what we need to know
- PMID: 27487772
- PMCID: PMC4972967
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-016-0513-0
IABP: history-evolution-pathophysiology-indications: what we need to know
Abstract
Treatment with the intraaortic balloon pump (IABP) is the most common form of mechanical support for the failing heart. Augmentation of diastolic pressure during balloon inflation contributes to the coronary circulation and the presystolic deflation of the balloon reduces the resistance to systolic output. Consequently, the myocardial work is reduced. The overall effect of the IABP therapy is an increase in the myocardial oxygen supply/demand ratio and thus in endocardial viability.This is an overall synopsis of what we need to know regarding IABP. Furthermore, this review article attempts to systematically delineate the pathophysiology linked with the hemodynamic consequences of IABP therapy. The authors also look at the future of the use of the balloon pump and conclude that the positive multi-systemic hemodynamic regulation during IABP treatment should further justify its use.
Keywords: Internal counterpulsation; Intra-aortic balloon pump; Mechanical circulatory support.
Figures
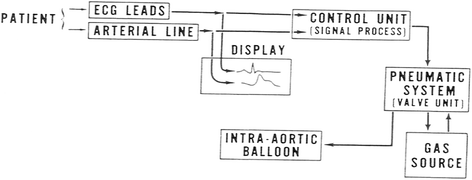
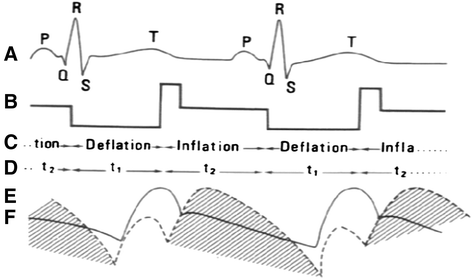
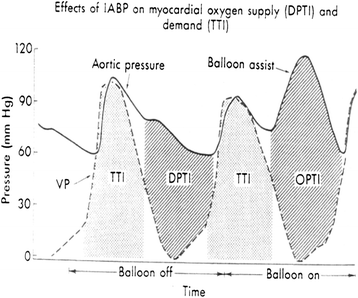
References
-
- Freedman RJ. The intra-aortic ballon pump system: current roles and future directions. J Appl Cardiol. 1991;6:313.
-
- Buckberg GD, Towers B, Paglia DE. Subendocardial Ischemia after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1972;5(64):669–84. - PubMed
-
- Krishna M, Zacharowski K. Principles of intra-aortic balloon pump counterpulsation. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain. 2009;9(1):24–28. doi: 10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkn051. - DOI
-
- Gelsomino S, Renzulli A, Rubino A, et al. effects of 1:1, 1:2, 1:3 intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation/heart support on coronary haemodynamics and cardiac contractile efficiency in an animal model of myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion. Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg. 2012;42(2):325–332. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezr327. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

