Retinoic Acid Improves Incidence and Severity of Necrotizing Enterocolitis by Lymphocyte Balance Restitution and Repopulation of LGR5+ Intestinal Stem Cells
- PMID: 27488085
- PMCID: PMC5167667
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000713
Retinoic Acid Improves Incidence and Severity of Necrotizing Enterocolitis by Lymphocyte Balance Restitution and Repopulation of LGR5+ Intestinal Stem Cells
Abstract
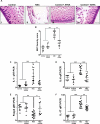
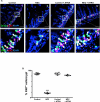
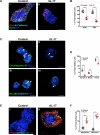
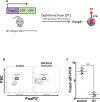
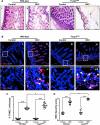
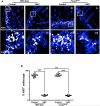
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the most devastating gastrointestinal disease of the premature infant. We have recently shown that NEC development occurs after an increase in proinflammatory CD4Th17 (Th17) cells and reduced anti-inflammatory forkhead box P3 regulatory T cells (Tregs) to the premature small intestine of mice and humans, which can be experimentally reversed in mice by administration of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA). We have also shown that NEC is characterized by apoptosis of Lgr5-positive intestinal stem cells (ISCs-Lgr5 cells) within the crypts of Lieberkühn, which are subsequently essential for intestinal homeostasis. We now hypothesize that the normal lymphocyte balance within the lamina propria of the intestine can be achieved via administration of ATRA which restores mucosal integrity by preventing the loss of ISCs. Using both in vivo and in vitro strategies, we now demonstrate that Th17 recruitment and Treg depletion lead to increased apoptosis within ISC niches, significantly impairing proliferative capacity and mucosal healing. ATRA exerted its protective effects by preventing T cell imbalance, ultimately leading to the protection of the ISC pool preventing the development of NEC in mice. These findings raise the exciting possibility that dietary manipulations could prevent and treat NEC by modulating lymphocyte balance and the ISC pool within the newborn small intestine.
Figures

References
-
- Anand RJ, Leaphart CL, Mollen KP, Hackam DJ. The role of the intestinal barrier in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Shock. 2007;27(2):124–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

