Deletion of soluble epoxide hydrolase enhances coronary reactive hyperemia in isolated mouse heart: role of oxylipins and PPARγ
- PMID: 27488890
- PMCID: PMC5142160
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00237.2016
Deletion of soluble epoxide hydrolase enhances coronary reactive hyperemia in isolated mouse heart: role of oxylipins and PPARγ
Abstract
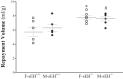
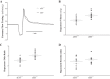
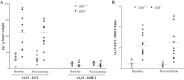
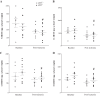
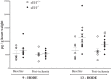
The relationship between soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and coronary reactive hyperemia (CRH) response to a brief ischemic insult is not known. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) exert cardioprotective effects in ischemia/reperfusion injury. sEH converts EETs into dihydroxyeicosatrienoic-acids (DHETs). Therefore, we hypothesized that knocking out sEH enhances CRH through modulation of oxylipin profiles, including an increase in EET/DHET ratio. Compared with sEH+/+, sEH-/- mice showed enhanced CRH, including greater repayment volume (RV; 28% higher, P < 0.001) and repayment/debt ratio (32% higher, P < 0.001). Oxylipins from the heart perfusates were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The 14,15-EET/14,15-DHET ratio was 3.7-fold higher at baseline (P < 0.001) and 5.6-fold higher post-ischemia (P < 0.001) in sEH-/- compared with sEH+/+ mice. Likewise, the baseline 9,10- and 12,13-EpOME/DiHOME ratios were 3.2-fold (P < 0.01) and 3.7-fold (P < 0.001) higher, respectively in sEH-/- compared with sEH+/+ mice. 13-HODE was also significantly increased at baseline by 71% (P < 0.01) in sEH-/- vs. sEH+/+ mice. Levels of 5-, 11-, 12-, and 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids were not significantly different between the two strains (P > 0.05), but were decreased postischemia in both groups (P = 0.02, P = 0.04, P = 0.05, P = 0.03, respectively). Modulation of CRH by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) was demonstrated using a PPARγ-antagonist (T0070907), which reduced repayment volume by 25% in sEH+/+ (P < 0.001) and 33% in sEH-/- mice (P < 0.01), and a PPARγ-agonist (rosiglitazone), which increased repayment volume by 37% in both sEH+/+ (P = 0.04) and sEH-/- mice (P = 0.04). l-NAME attenuated CRH in both sEH-/- and sEH+/+ These data demonstrate that genetic deletion of sEH resulted in an altered oxylipin profile, which may have led to an enhanced CRH response.
Keywords: coronary reactive hyperemia; dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids; epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; isolated perfused heart; oxylipins; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase on the Modulation of Coronary Reactive Hyperemia: Role of Oxylipins and PPARγ.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 1;11(9):e0162147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162147. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27583776 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Endothelial Over-Expression of Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (Tie2-sEH Tr) Attenuates Coronary Reactive Hyperemia in Mice: Role of Oxylipins and ω-Hydroxylases.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 5;12(1):e0169584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169584. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28056085 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced coronary reactive hyperemia in mice was reversed by the soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor (t-AUCB): Role of adenosine A2A receptor and plasma oxylipins.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017 Jul;131:83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017. PMID: 28890385 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between adenosine receptors and CYP450-derived oxylipins in the modulation of cardiovascular, including coronary reactive hyperemic response.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Dec;240:108213. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108213. Epub 2022 May 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35597366 Review.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase: gene structure, expression and deletion.Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):61-74. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 20. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23701967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of oxylipins in cardiovascular diseases.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Jul;39(7):1142-1154. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.24. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29877318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular endothelial overexpression of human CYP2J2 (Tie2-CYP2J2 Tr) modulates cardiac oxylipin profiles and enhances coronary reactive hyperemia in mice.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 22;12(3):e0174137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174137. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28328948 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Exacerbates Coronary Reactive Hyperemia Reduction in Angiotensin-II-Treated Mouse Hearts.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 1;83(1):46-54. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001490. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37788350 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the immunomodulator role of plasma oxidized lipids in SA-AKI progression: a CRRT perspective.Front Physiol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1412235. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1412235. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39764381 Free PMC article.
-
Ephx2-gene deletion affects acetylcholine-induced relaxation in angiotensin-II infused mice: role of nitric oxide and CYP-epoxygenases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Feb;465(1-2):37-51. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03665-x. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31797255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Shabrawey M, Mussell R, Kahook K, Tawfik A, Eladl M, Sarthy V, Nussbaum J, El-Marakby A, Park SY, Gurel Z, Sheibani N, Maddipati KR. Increased expression and activity of 12-lipoxygenase in oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy and proliferative diabetic retinopathy: implications in retinal neovascularization. Diabetes 60: 614–624, 2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altmann R, Hausmann M, Spottl T, Gruber M, Bull AW, Menzel K, Vogl D, Herfarth H, Scholmerich J, Falk W, Rogler G. 13-Oxo-ODE is an endogenous ligand for PPARγ in human colonic epithelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol 74: 612–622, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

