Platelets in Pulmonary Immune Responses and Inflammatory Lung Diseases
- PMID: 27489307
- PMCID: PMC6345245
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00038.2015
Platelets in Pulmonary Immune Responses and Inflammatory Lung Diseases
Abstract
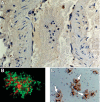
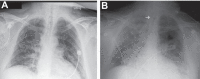
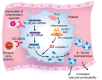
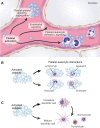
Platelets are essential for physiological hemostasis and are central in pathological thrombosis. These are their traditional and best known activities in health and disease. In addition, however, platelets have specializations that broaden their functional repertoire considerably. These functional capabilities, some of which are recently discovered, include the ability to sense and respond to infectious and immune signals and to act as inflammatory effector cells. Human platelets and platelets from mice and other experimental animals can link the innate and adaptive limbs of the immune system and act across the immune continuum, often also linking immune and hemostatic functions. Traditional and newly recognized facets of the biology of platelets are relevant to defensive, physiological immune responses of the lungs and to inflammatory lung diseases. The emerging view of platelets as blood cells that are much more diverse and versatile than previously thought further predicts that additional features of the biology of platelets and of megakaryocytes, the precursors of platelets, will be discovered and that some of these will also influence pulmonary immune defenses and inflammatory injury.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Alexander JS, Patton WF, Christman BW, Cuiper LL, Haselton FR. Platelet-derived lysophosphatidic acid decreases endothelial permeability in vitro. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol : H115–H122, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Alitalo K. The lymphatic vasculature in disease. Nature Med : 1371–1380, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Ammon C, Kreutz M, Rehli M, Krause SW, Andreesen R. Platelets induce monocyte differentiation in serum-free coculture. J Leukocyte Biol : 469–476, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Anabel AS, Eduardo PC, Pedro Antonio HC, Carlos SM, Juana NM, Honorio TA, Nicolas VS, Sergio Roberto AR. Human platelets express Toll-like receptor 3 and respond to poly I:C. Hum Immunol : 1244–1251, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

