N-glycosylation in the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius involves a short dolichol pyrophosphate carrier
- PMID: 27490243
- PMCID: PMC5039095
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.12341
N-glycosylation in the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius involves a short dolichol pyrophosphate carrier
Abstract
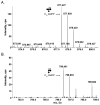
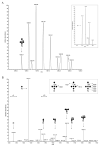
N-glycosylation is a post-translational modification that occurs across evolution. In the thermoacidophilic archaea Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, glycoproteins are modified by an N-linked tribranched hexasaccharide reminiscent of the N-glycans assembled in Eukarya. Previously, hexose-bearing dolichol phosphate was detected in a S. acidocaldarius Bligh-Dyer lipid extract. Here, we used a specialized protocol for extracting lipid-linked oligosaccharides to detect a dolichol pyrophosphate bearing the intact hexasaccharide, as well as its biosynthetic intermediates. Furthermore, evidence for N-glycosylation of two S. acidocaldarius proteins by the same hexasaccharide and its derivatives was collected. These findings thus provide novel insight into archaeal N-glycosylation.
Keywords: N-glycosylation; Sulfolobus acidocaldarius; archaea; dolichol; thermoacidophile.
© 2016 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

