The economic costs of mental disorders: Do our societies react appropriately to the burden of mental disorders?
- PMID: 27491723
- PMCID: PMC5007565
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201642951
The economic costs of mental disorders: Do our societies react appropriately to the burden of mental disorders?
Abstract
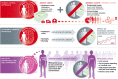
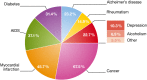
Mental disorders affect a huge number of people and have a major economic impact due to treatment costs and lost productivity. Society and politics need to acknowledge this huge toll in order to better support the healthcare systems that deal with these disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Wittchen HU, Jacobi F, Rehm J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Jonsson B, Olesen J, Allgulander C, Alonso J, Faravelli C et al (2011) The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21: 655–679 - PubMed
-
- Patel V, Chisholm D, Parikh R, Charlson FJ, Degenhardt L, Dua T, Ferrari AJ, Hyman SE, Laxminarayan R, Levin C et al (2016) Global priorities for addressing the burden of mental, neurological, and substance use disorders In Mental, neurological, and substance use disorders, Patel V, Chisholm D, Dua T, Laxminarayan R, Medina‐Mora ME. (eds), pp 1–27. Washington, DC: The World Bank; - PubMed
-
- Whiteford HA, Degenhardt L, Rehm J, Baxter AJ, Ferrari AJ, Erskine HE, Charlson FJ, Norman RE, Flaxman AD, Johns N et al (2013) Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 382: 1575–1586 - PubMed
-
- Hu T (2004) An international review of the economic costs of mental illness. World Bank Working Paper 31
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

