Patterns of diaphragm function in critically ill patients receiving prolonged mechanical ventilation: a prospective longitudinal study
- PMID: 27492005
- PMCID: PMC4974210
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-016-0179-8
Patterns of diaphragm function in critically ill patients receiving prolonged mechanical ventilation: a prospective longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: In intensive care unit (ICU) patients, diaphragmatic dysfunction (DD) can occur on admission or during the subsequent stay. The respective incidence of these two phenomena has not been previously studied in humans. The study was designed to describe temporal trends in diaphragm function in mechanically ventilated (MV) patients.
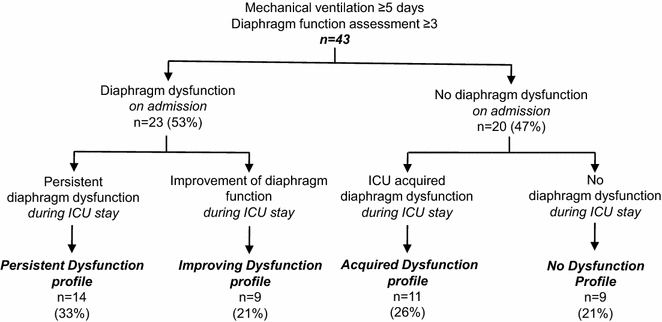
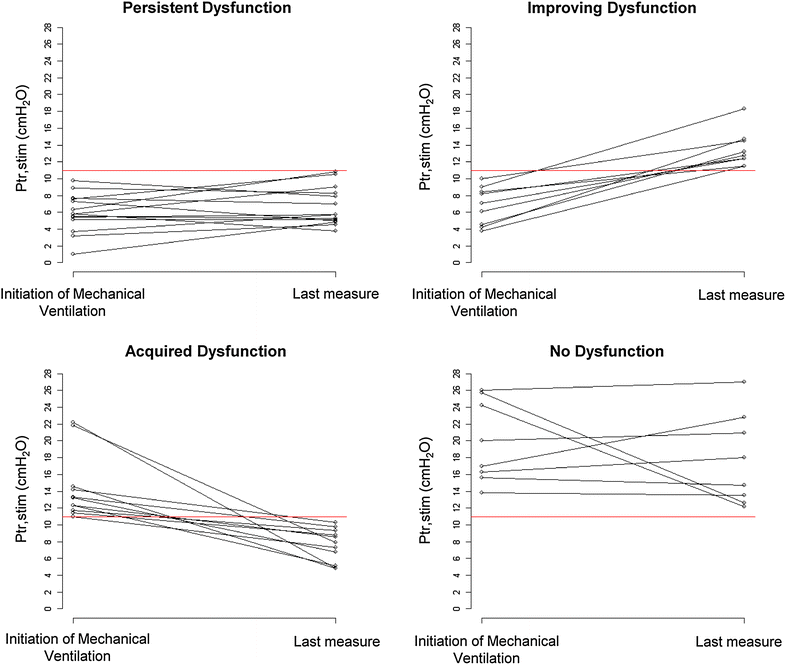
Methods: Ancillary study of a prospective, 6-month, observational cohort study conducted in two ICUs. MV patients were studied within 24 h following intubation (day-1) and every 48-72 h thereafter. Diaphragm function was assessed by twitch tracheal pressure (Ptr,stim) in response to bilateral anterior magnetic phrenic nerve stimulation. Diaphragm dysfunction was defined as Ptr,stim < 11 cmH2O. Patients who received MV for at least 5 days were retained, and the first and the last measures were analysed.
Results: Forty-three patients were included. Overall, 79 % of patients developed DD at some point during their ICU stay: 23 (53 %) patients presented DD on initiation of mechanical ventilation, 14 (33 %) of whom had persistent DD, while diaphragm function improved in 9 (21 %). Among the remaining 20 (47 %) patients who did not present DD on initiation of MV, 11 (26 %) developed DD during the ICU stay, while 9 (21 %) did not. Mortality was higher in patients with DD either on initiation of mechanical ventilation or during the subsequent ICU stay than in those who never developed DD (35 vs. 0 %, p = 0.04). Duration of MV was higher in patients with DD on initiation of MV that subsequently persisted than in patients who never exhibited diaphragm dysfunction (18 vs. 5 days, p = 0.04). Factors associated with a change in Ptr,stim were: age [linear coefficient regression (Coeff.) -0.097, standard error (SD) 0.047, p = 0.046], PaO2/FiO2 ratio (Coeff. 0.014, SD 0.006, p = 0.0211) and the proportion of the time under MV with sedation (per 10 %, Coeff. -5.359, SD 2.451, p = 0.035).
Conclusions: DD is observed in a large majority of MV patients ≥5 days at some point of their ICU stay. Various patterns of DD are observed, including DD on initiation of mechanical ventilation and ICU-acquired DD. Trial registration clinicaltrials.gov Identifier # NCT00786526.
Keywords: Diaphragm Respiratory muscles function; Intensive care unit; Mechanical ventilation; Outcome; Phrenic nerve stimulation; Sepsis.
Figures
References
-
- Demoule A, Jung B, Prodanovic H, Molinari N, Chanques G, Coirault C, et al. Diaphragm dysfunction on admission to the intensive care unit. Prevalence, risk factors, and prognostic impact-a prospective study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188:213–219. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201209-1668OC. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical